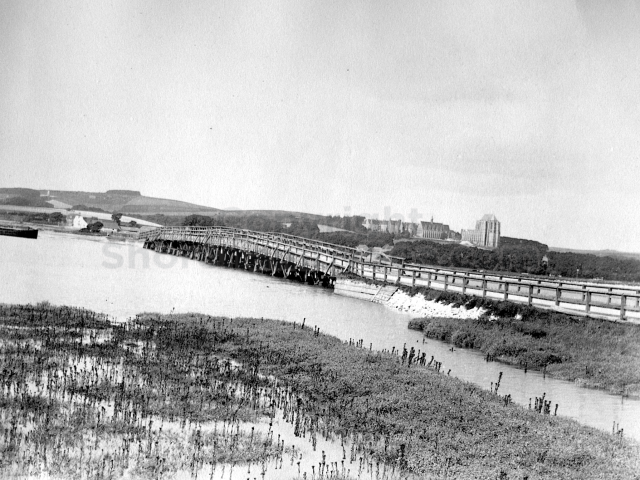
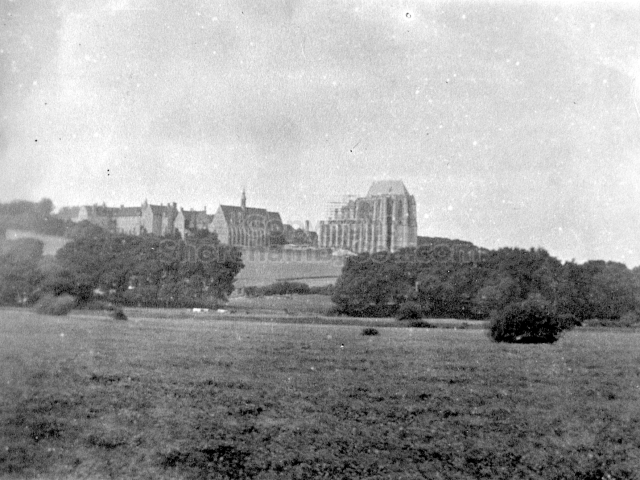
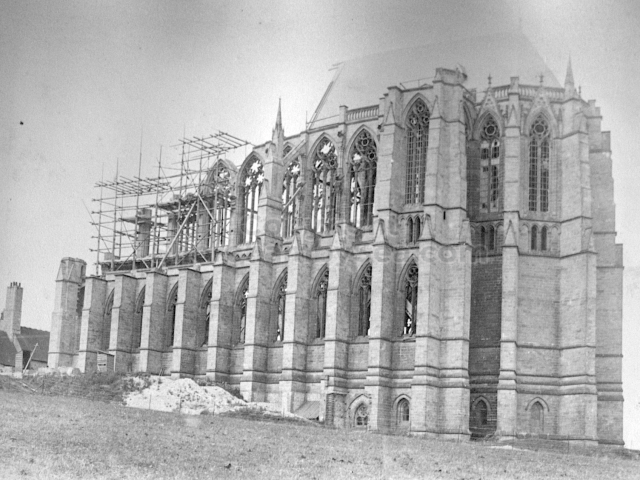
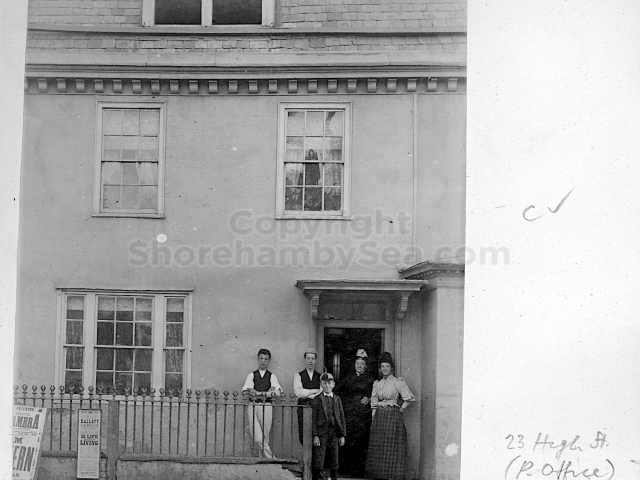
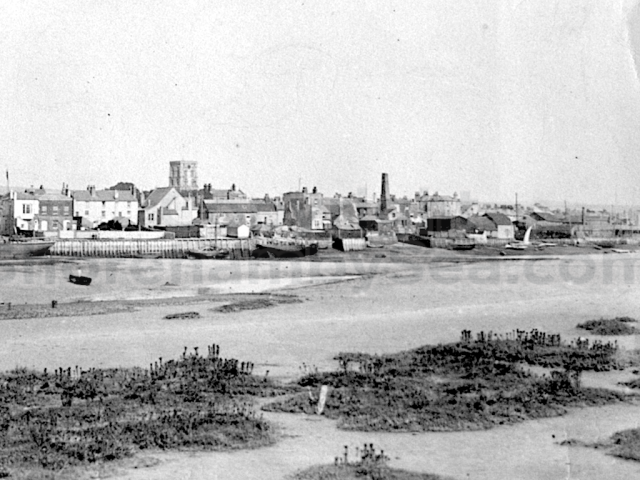
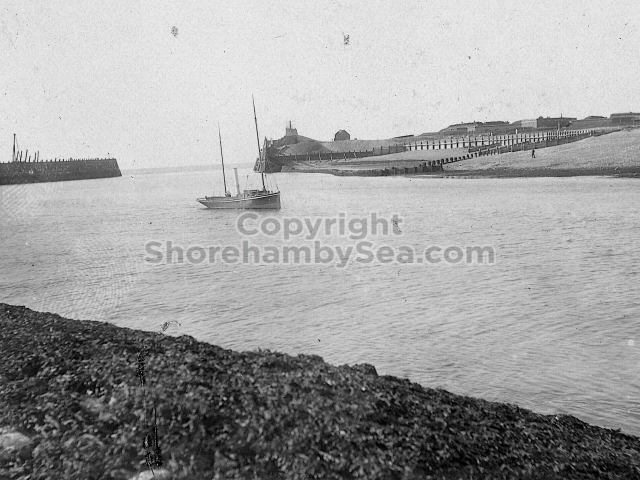
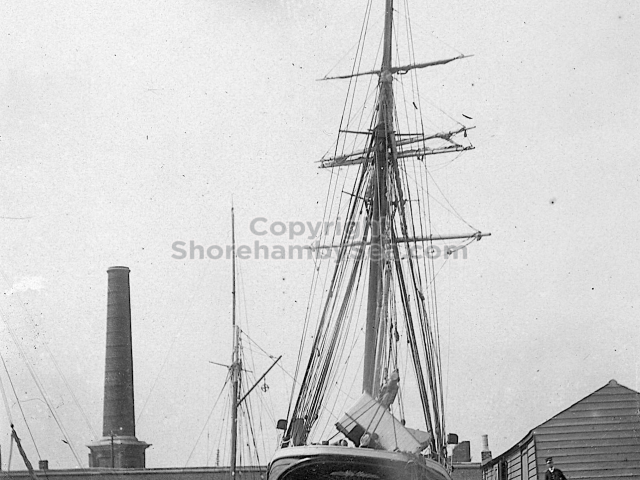
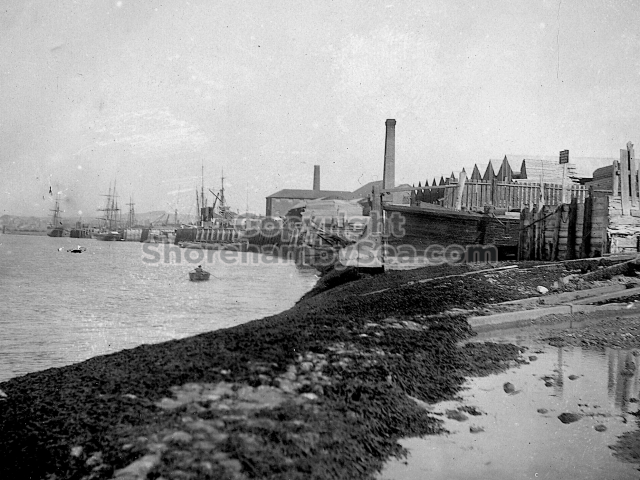
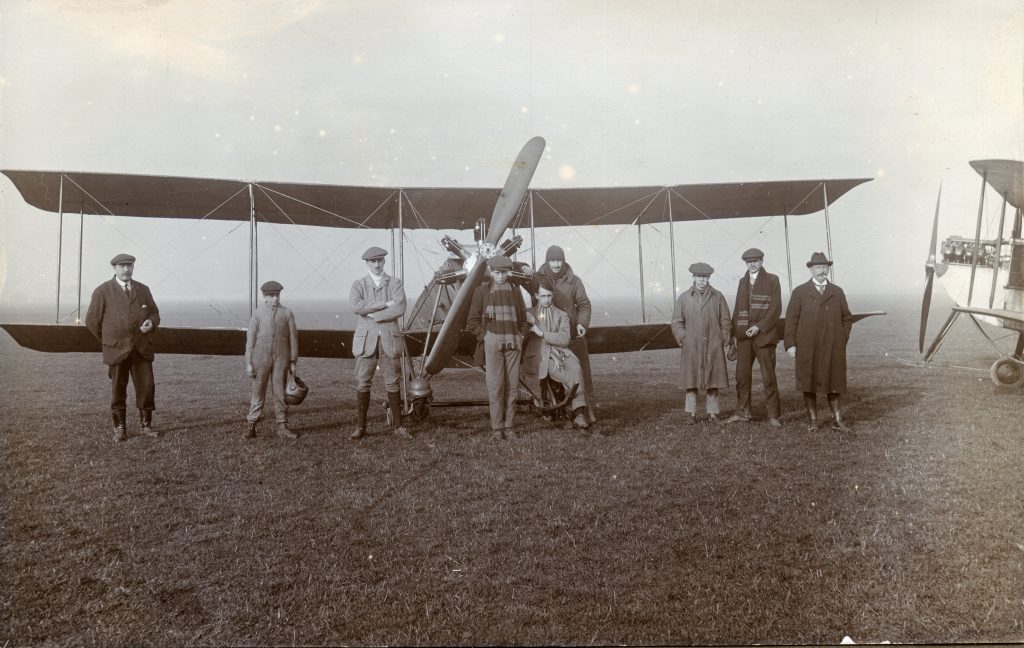
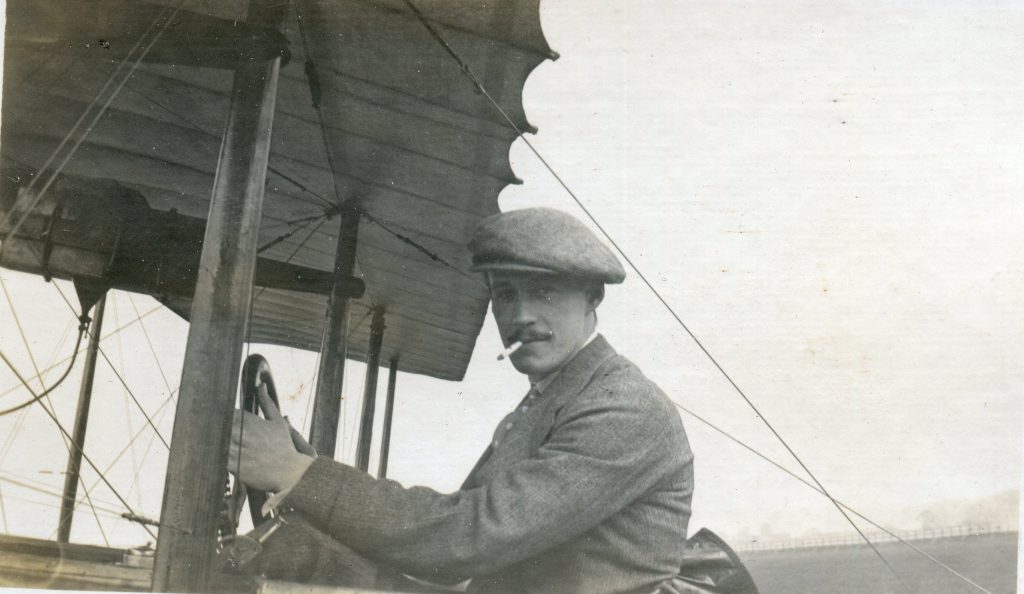
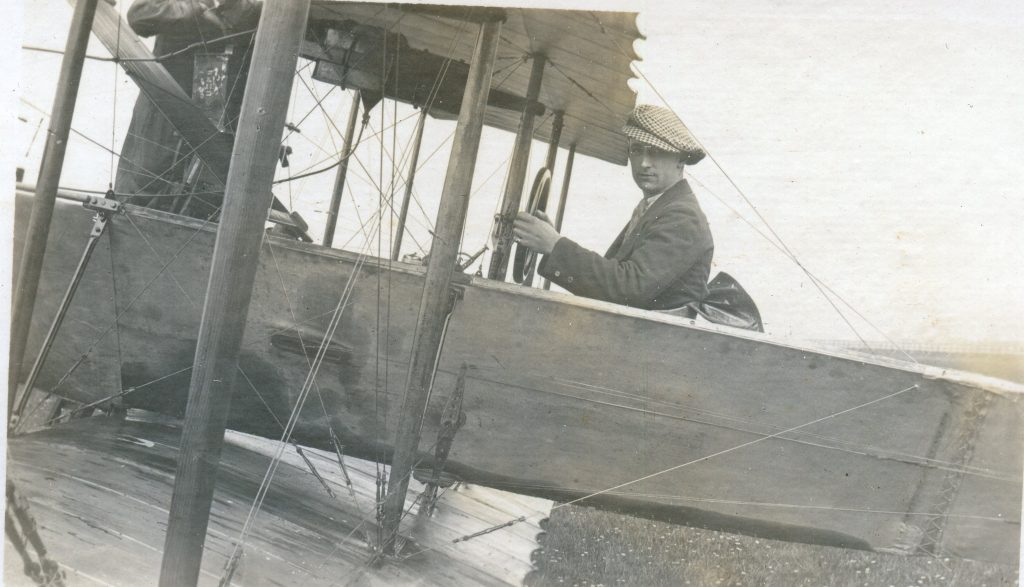
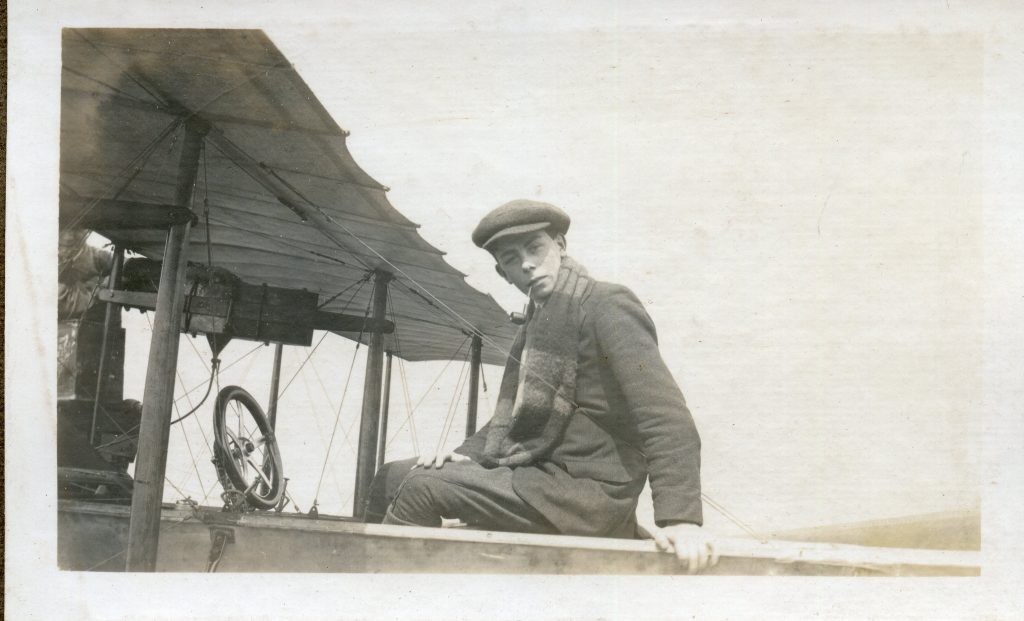
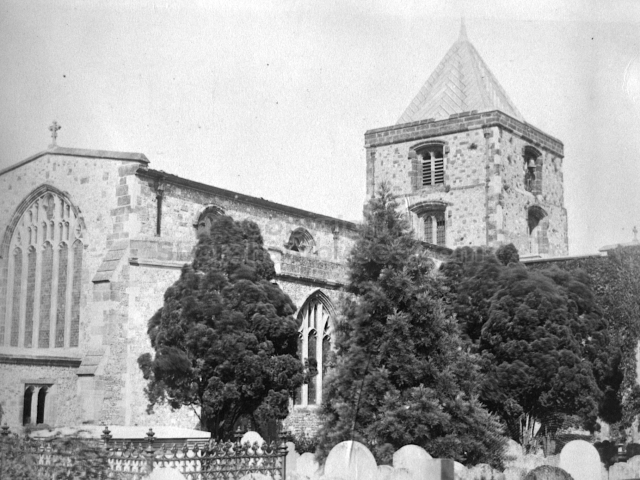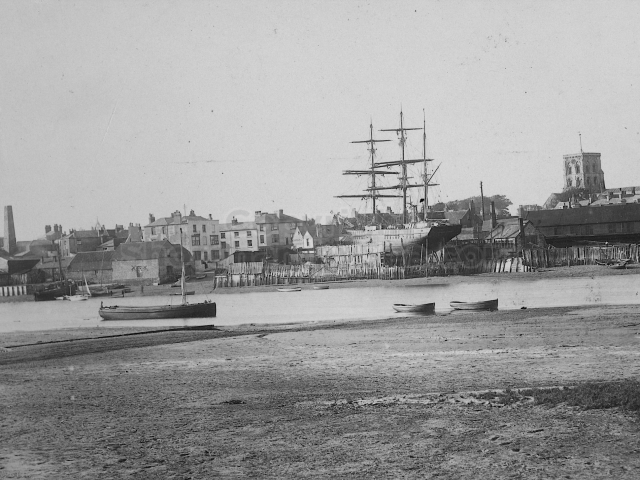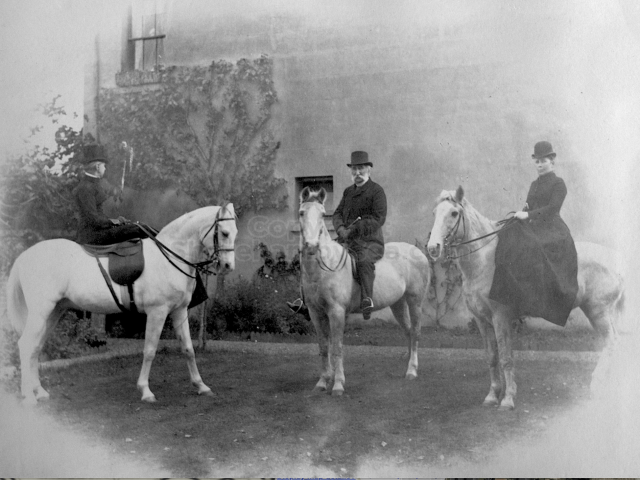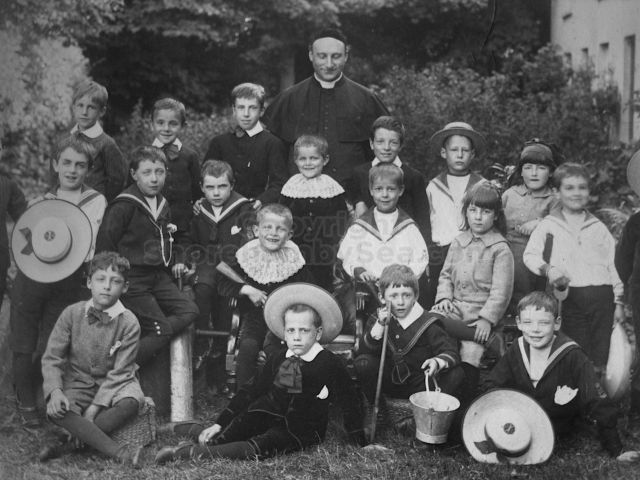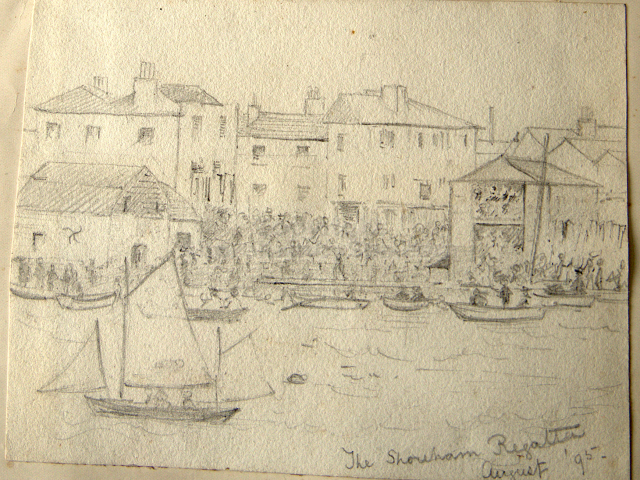The Buckingham Book
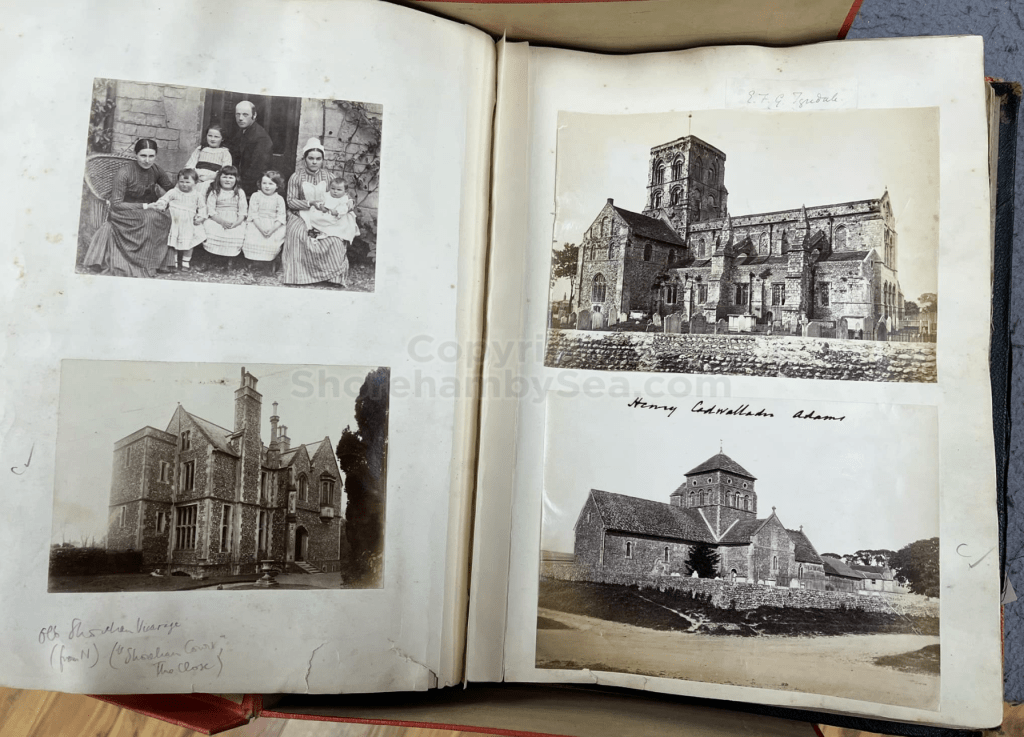

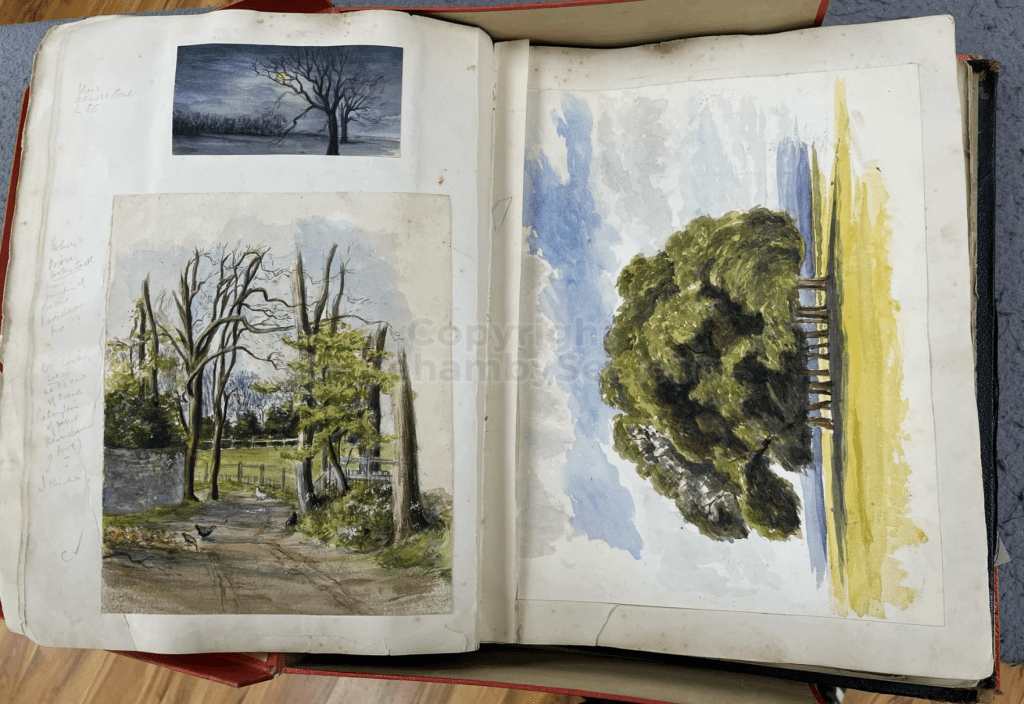
In 2025 a Shoreham resident acquired at auction a significant historical find. It was a rather battered leather bound family scrapbook dating from 1889. It contained photographs, sketches, and cuttings collected by the Head family of Great Buckingham, Old Shoreham. The story behind the “Buckingham Book” book is tantalising. It had been kept in the Head family’s possession for 80 years but had been torn in two, and separated, with the front part donated to a museum. The second part had been given by the family to a local historian Michael Norman. He was keen for the 2 halves to be reunited but his untimely death in 2013 meant the book was forgotten and eventually sold at auction. 13 years later and we now have possession of that second half along with its accompanying covering letter from Michael Norman. The images in the book are in this gallery.

The background to the Head family
We can surmise that the book was split in 1983 after Hester’s death. Whilst it is reasonable to assume the Marlipins Museum holds the other half of the book they are currently unable to confirm this.
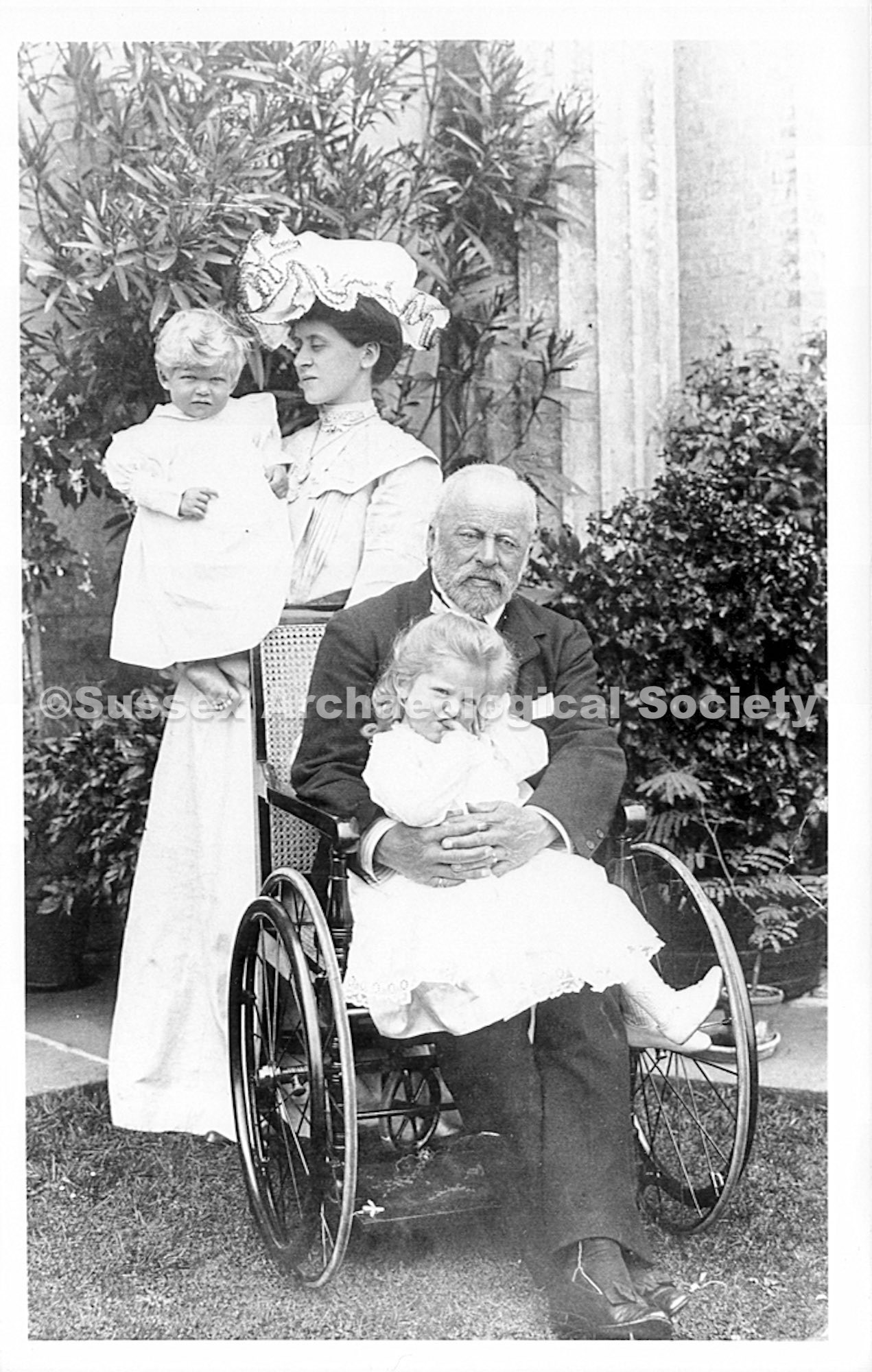
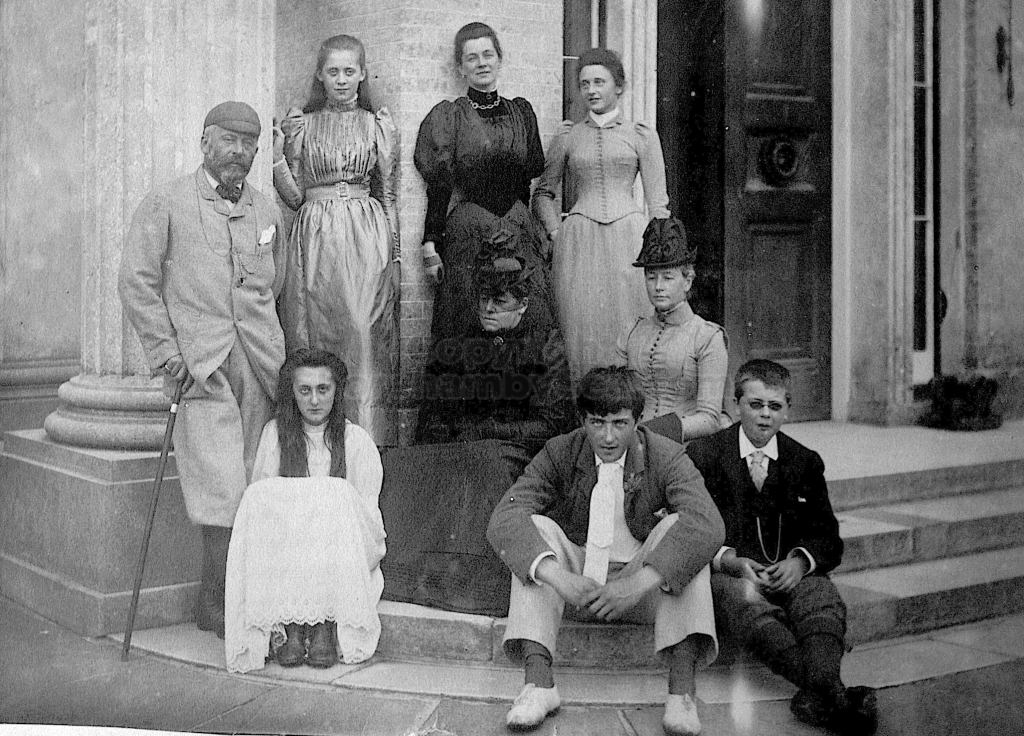


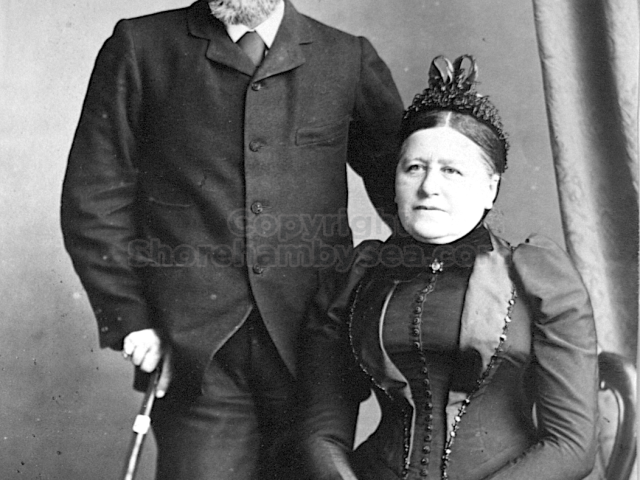
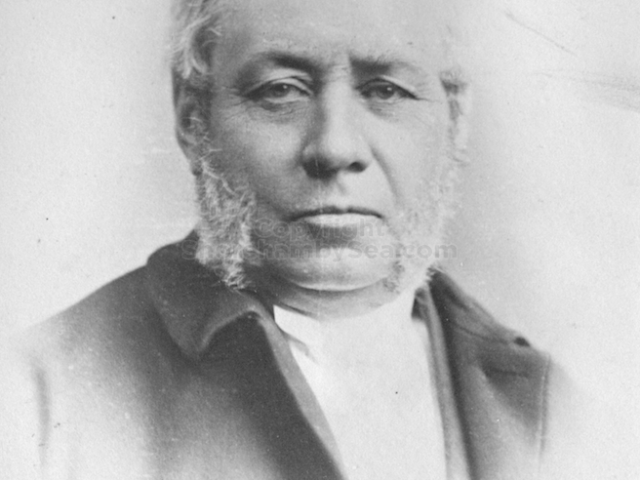
Hester’s father was Henry Head b.1834 m.1860 Died 1st July 1905
Hester’s mother was Hester Head (née Beck) b.1835 m.1860 d.1907
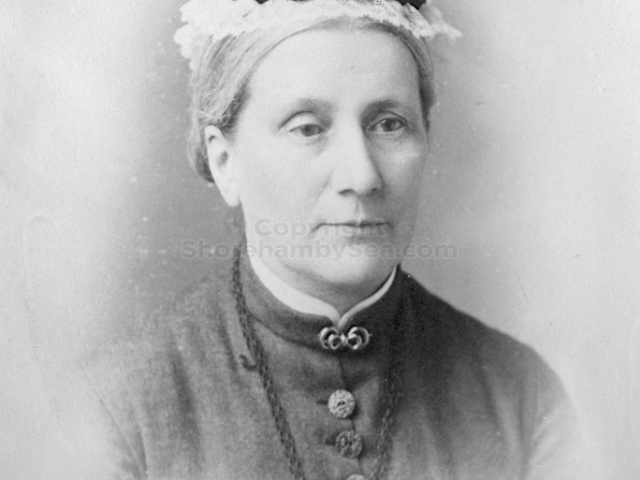
Hester became Hester Pinney (née Head Jnr.) by marriage in 1900 b.1875 d.1958
Hester’s daughter Hester Harriott Marsden-Smedley (née Pinney) b. Ponna India 21st June 1901. Married Basil Futvoye Marsden-Smedley 1927. Hester died in 1982 in Chelsea.
Hester’s daughter was Henrietta Hester Marsden-Smedley b.1935 d.1998
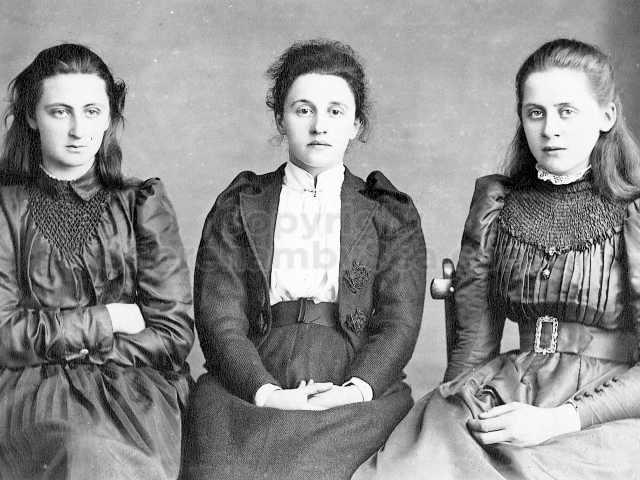
Sons and daughters of Henry and Hester Head:
- Sir Henry Head1 b. 4 Aug 1861, edu: Charterhouse, Trinity Coll Camb. d. 8 Oct 1940
- Charles Howard Head1 b. 28 Dec 1862, edu: Charterhouse d. 6 Dec 1877 died of pneumonia at Charterhouse school age 14 (Godalming)
- Hugh Stanley Head1 b. 9 Jun 1864, edu: Charterhouse d. 4 Nov 1890 age 26 (old Shoreham)
- Rachel Mary Head1 b. 26 Aug 1865, d. 19 Jan 1870 age 4
- Katherine Head1 b. 17 Sep 1866, d. 2 Aug 1869 age 3
- Francis Head1 b. 13 Feb 1868, edu: Lancing College d. 11 Feb 1905 of brain tumour age 36
- Christopher Head1 b. 25 Dec 1869, edu: Lancing College, Trinity Coll. Camb d. 15 Apr 1912 on Titanic age 43
- Geoffrey Head+1 b. 14 Apr 1872, edu: Lancing College d. 22 Nov 1955
- John Alban Head1 b. 7 Dec 1873, edu: Lancing College d. 8 Jun 1931 age 57
- Hester Head+1 b. 29 Jan 1875, d. 1958
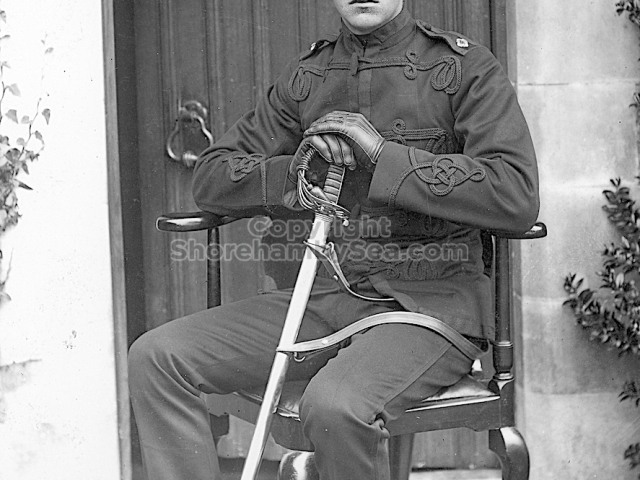
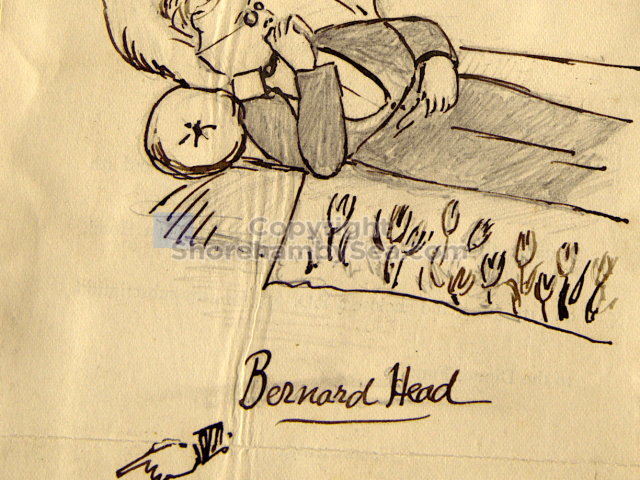
- Bernard Head1 b. 12 Jan 1876, d. 13 Aug 1915 Major, Corps: Royal Welsh Fusiliers killed in action at Gallipoli age 39
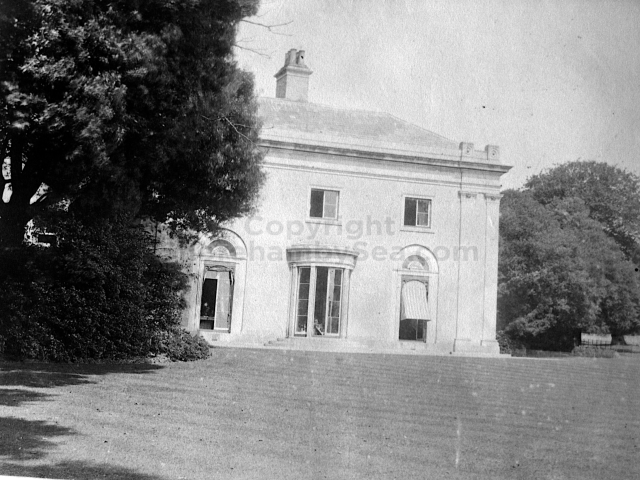
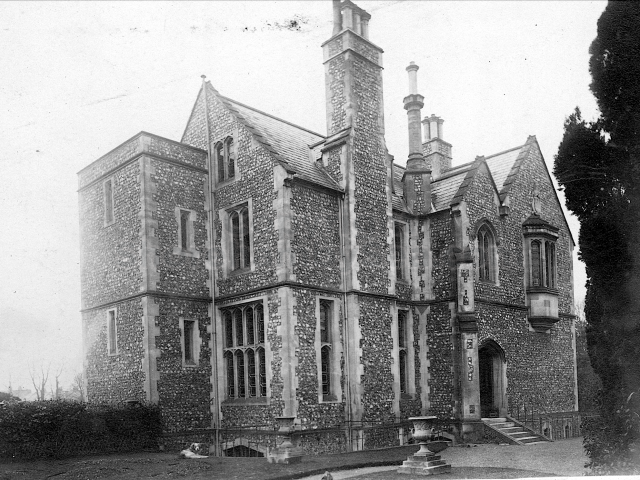
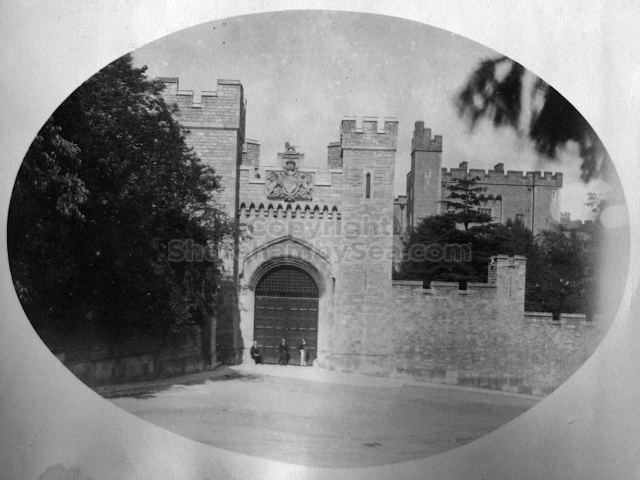
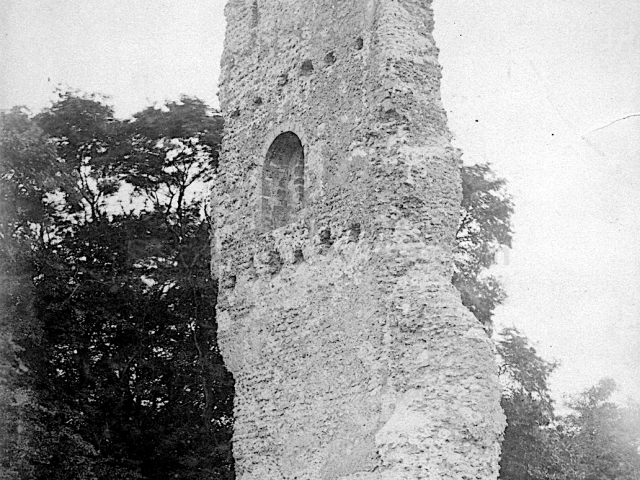
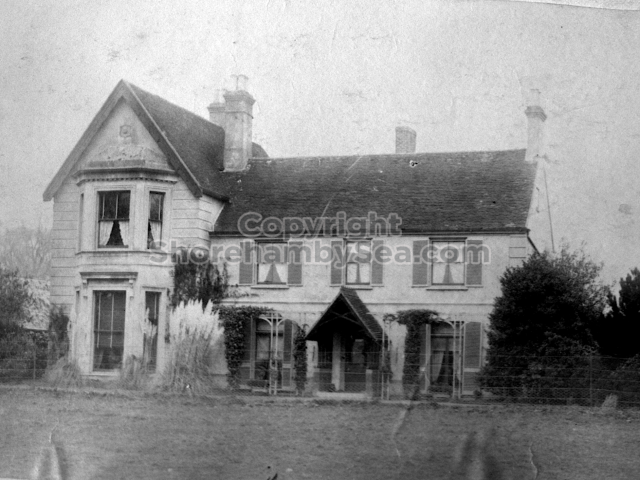
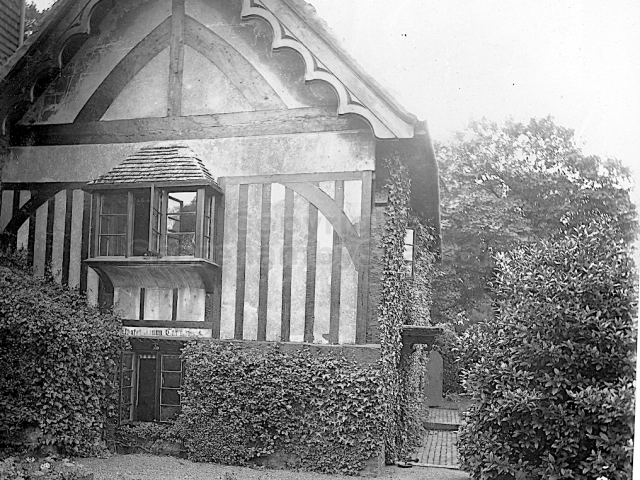
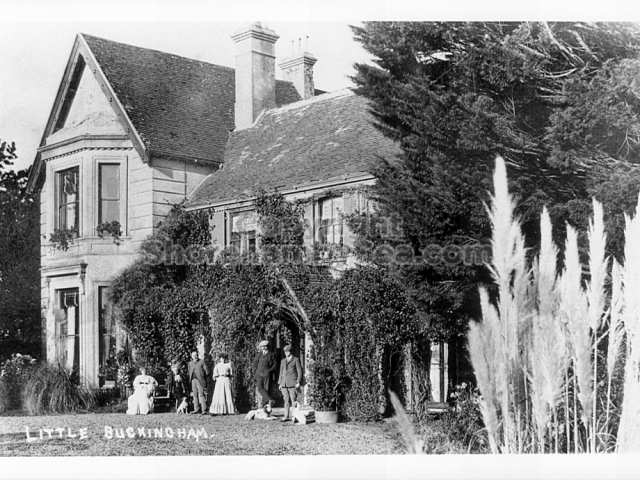
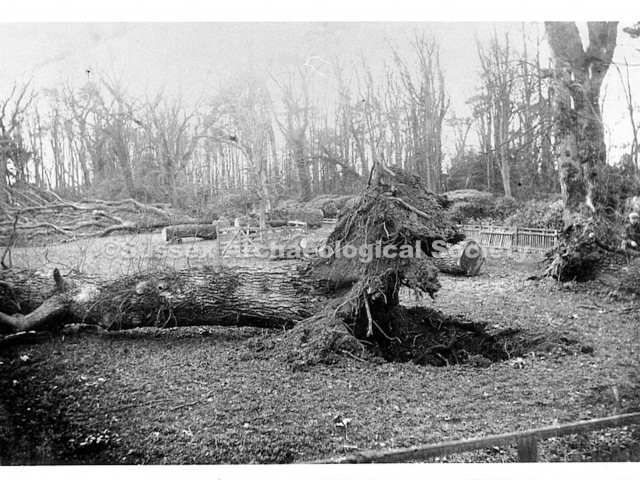
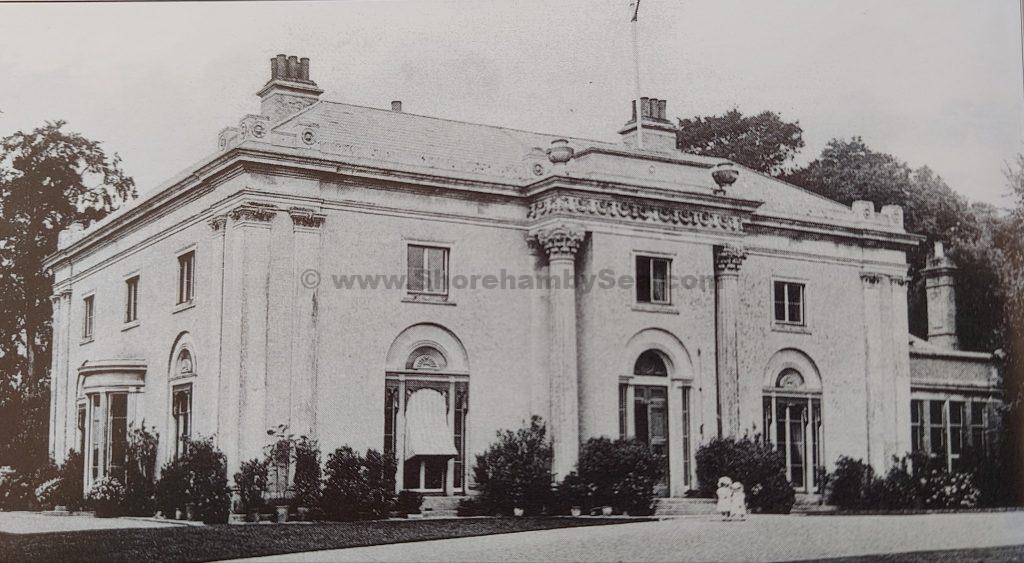
Henry Head died in July 1905 of heart disease, 5 months after the death of his 4th son Francis from a brain tumour at the age 36. This was the catalyst for the abandonment of Buckingham House that became a ruin by 1910.
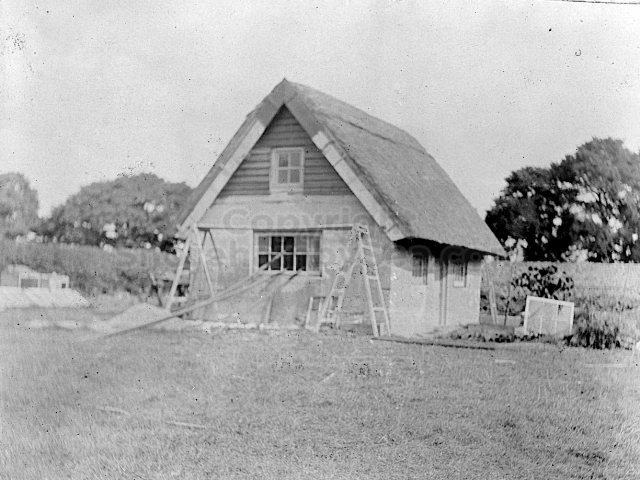
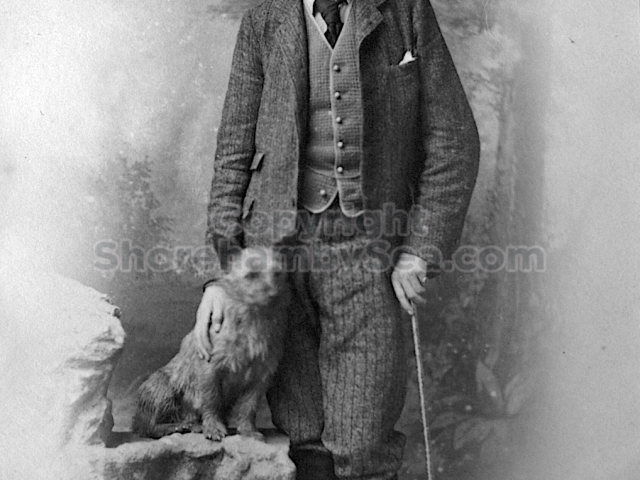
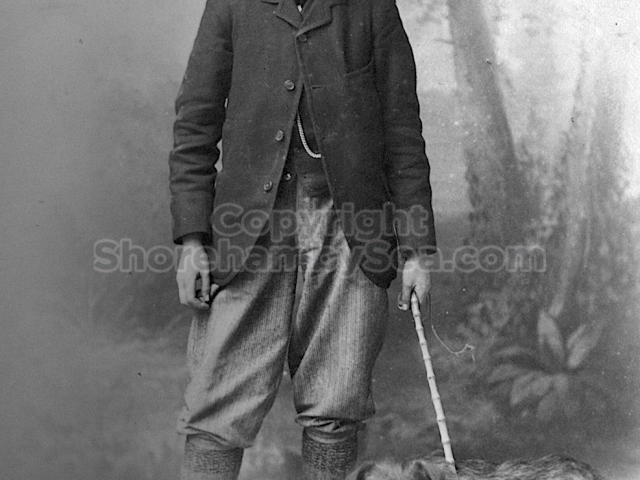
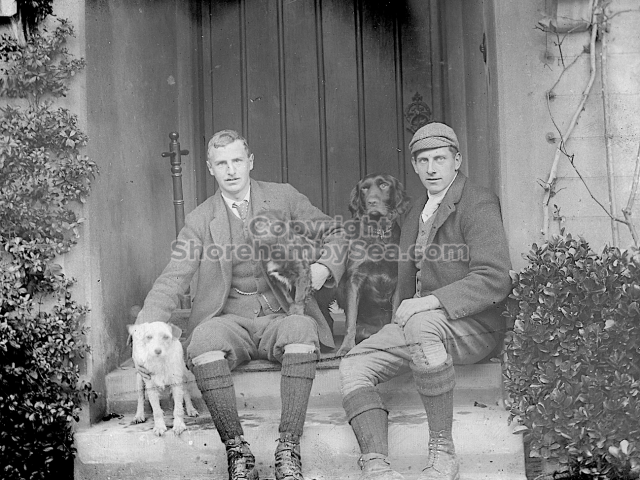
The contents of the Buckingham Book ( the 2nd half)
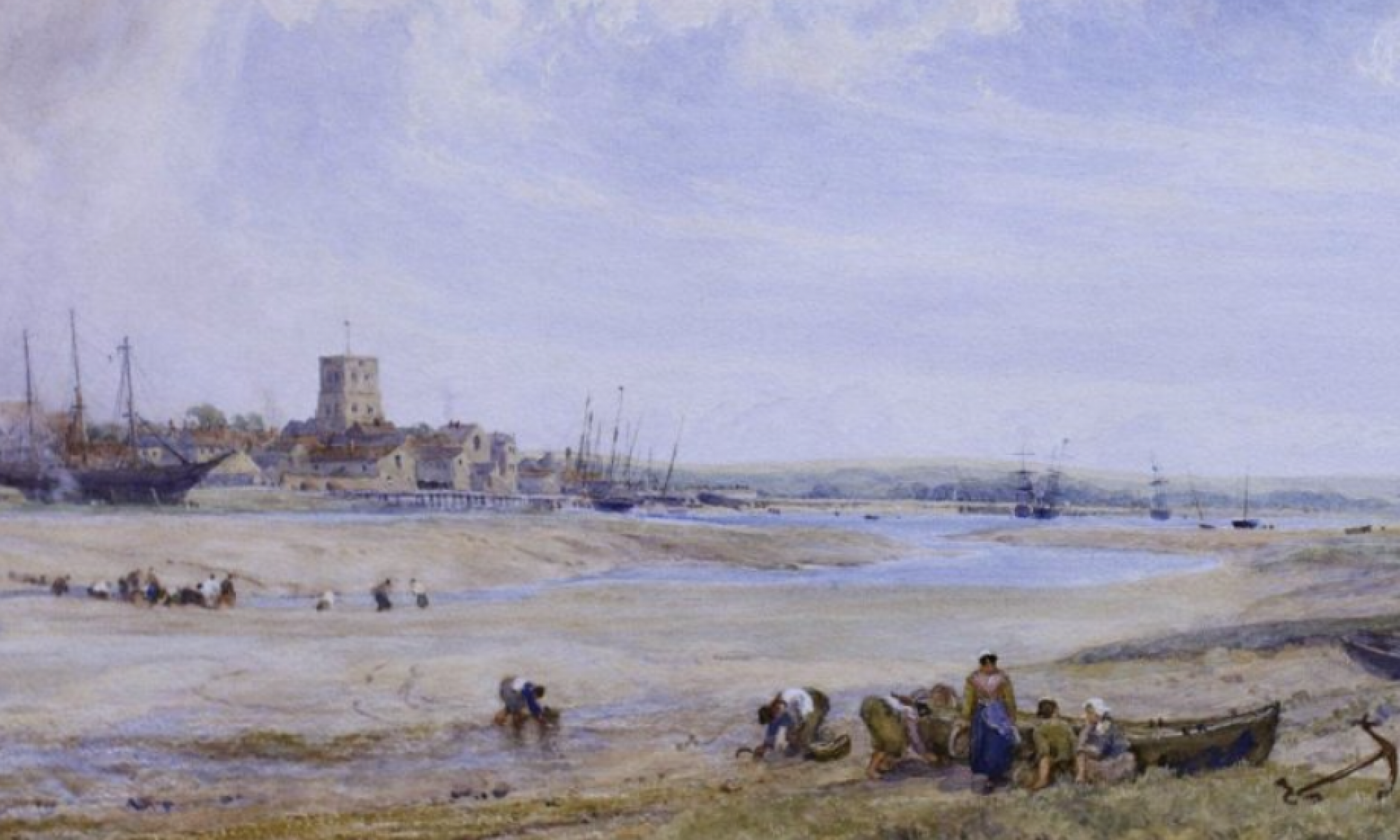
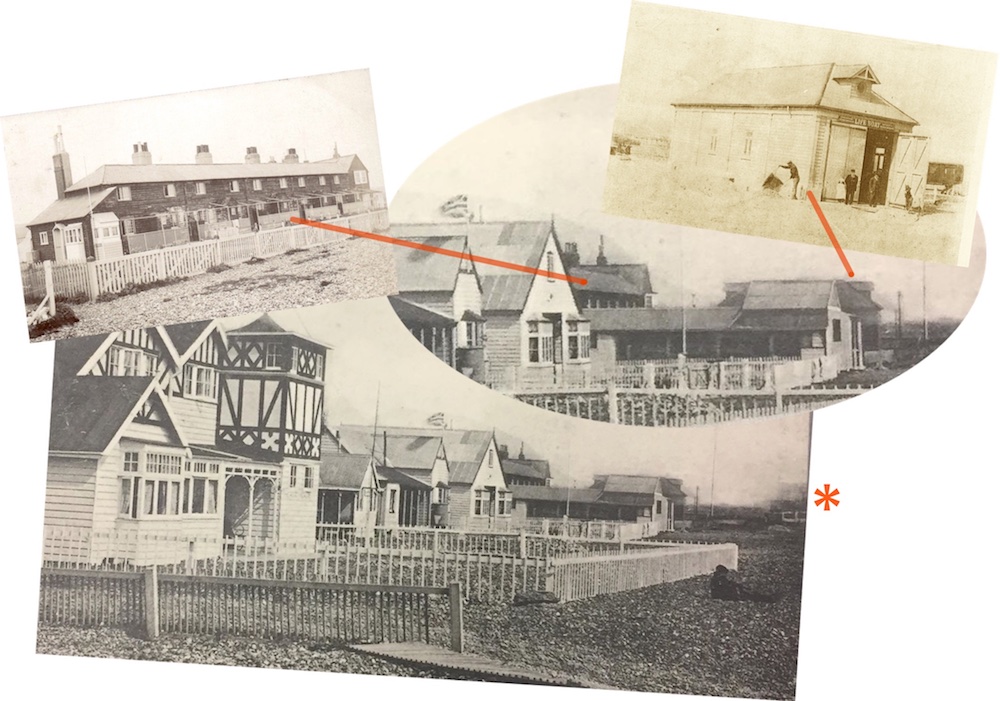
The mystery of what happened to the first half of The Buckingham Book is perhaps explained by a number of photos in the SAS / Marlipins Collection of images. Whilst there seems to be just 11 images they are of a similar nature to those in the second half of the book. The suggestion is these 11 were cherry picked by SAS and the rest of the book is in their archive awaiting full scrutiny and publication.
Selection from the front half of the Buckingham Book
Covering letter:
This Family Scrapbook compiled by the Head Family to record their time at Buckingham (Buckingham House, Old Shoreham) from 1889 to 1905 was in the possession of Lady (Hester) Marsden-Smedley (née Pinney), the daughter of Lady Hester Pinney (née Head). Before she died, Lady Pinney stated that she wanted me to have it because of its relevance to Shoreham. In due course I made contact with her daughter in Chelsea and arranged to go up to collect it.
Perhaps not surprisingly, Lady Marsden-Smedley would have liked to have kept it, since it contained so much of Family interest. In the event, she simply tore the book in half and gave me the front part, and this I placed in Marlipins. It may since have been dismembered, which is a great pity.
The other half I was very surprised to be offered many years later through a friend. and bought it, at a price, and did not enquire as to its provenance. I still have it, in its somewhat battered slate.
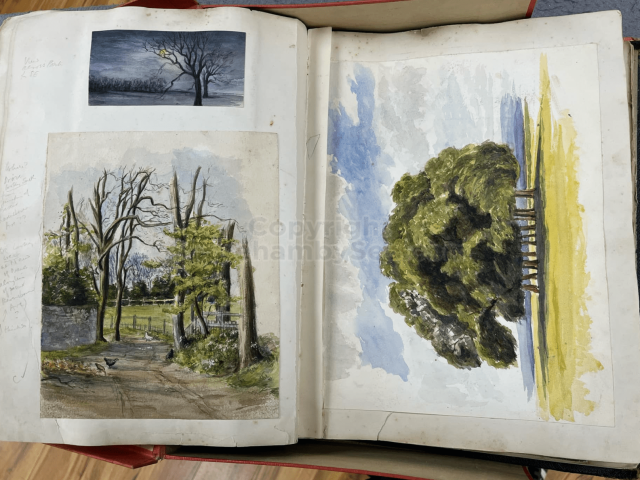
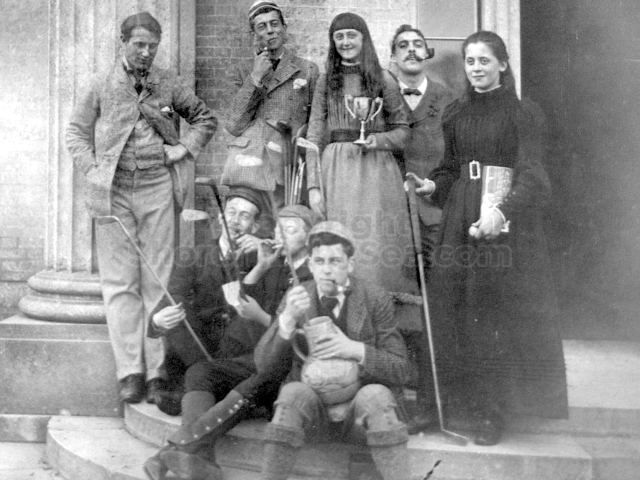
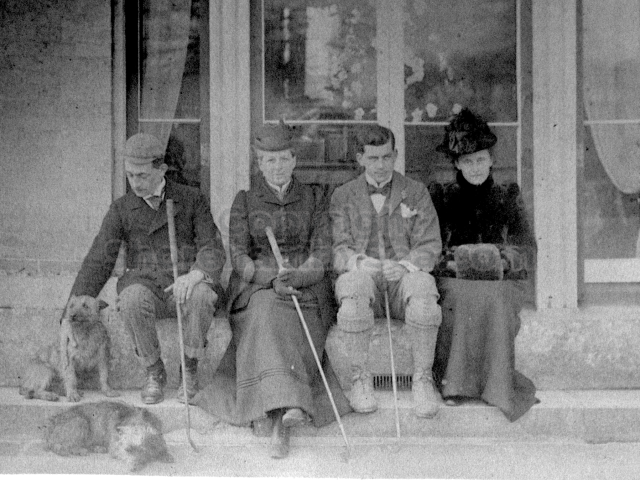
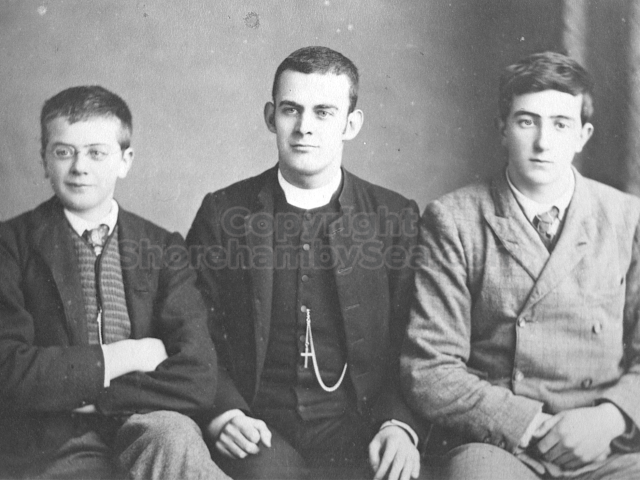
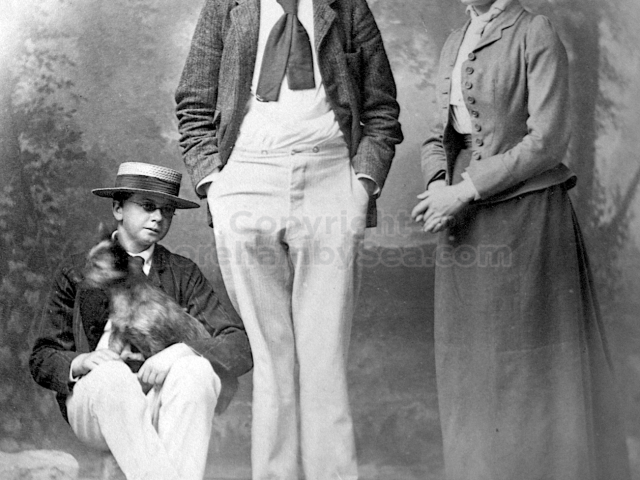
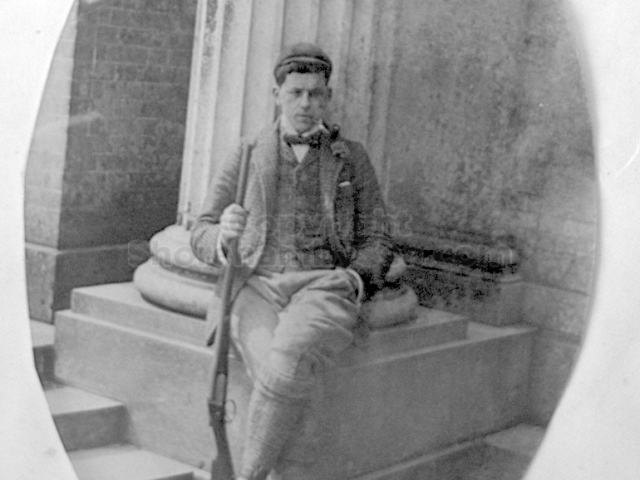
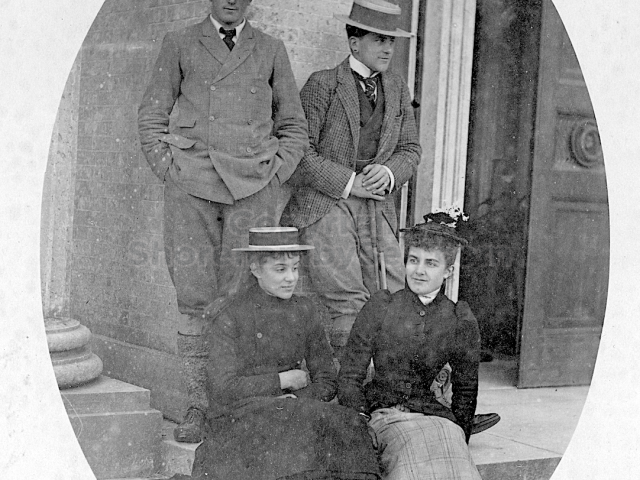
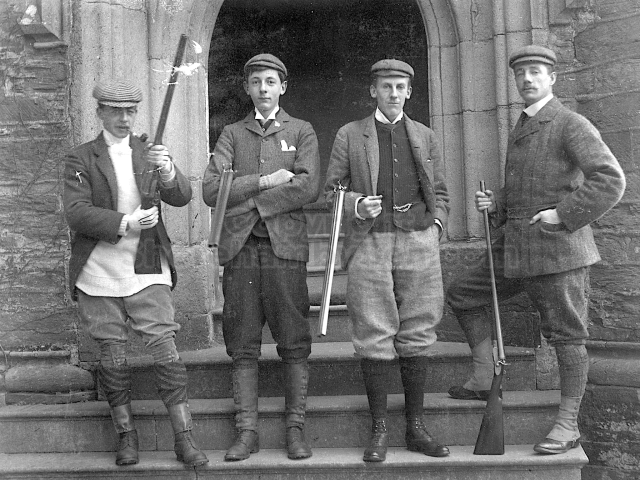
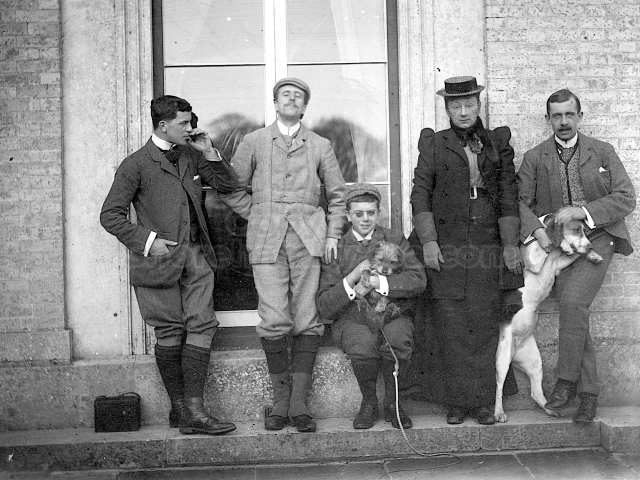
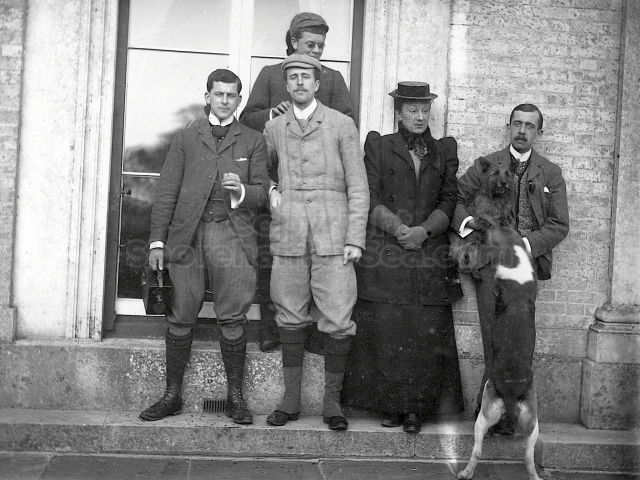
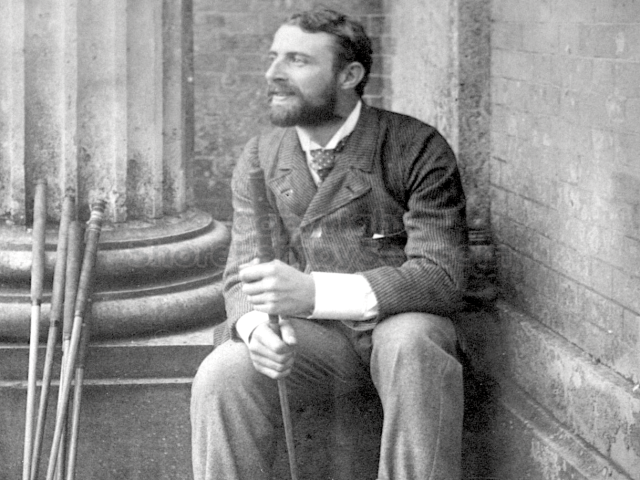
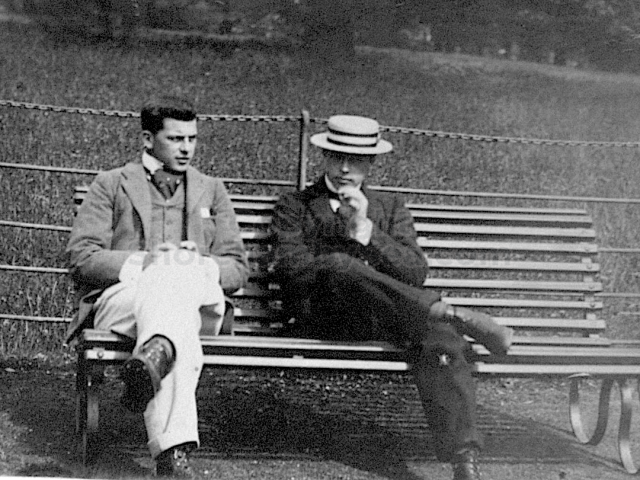
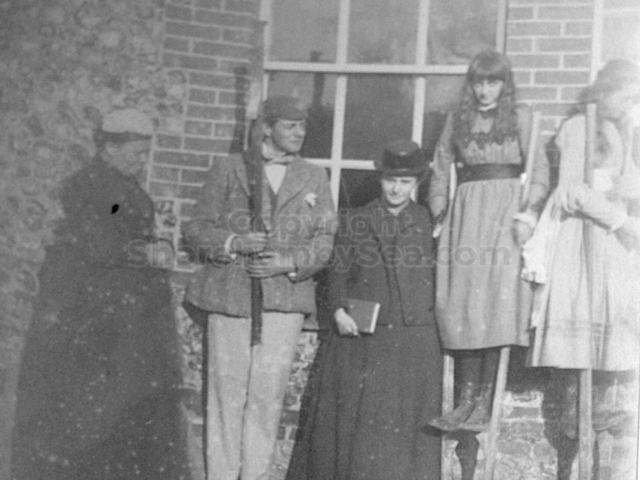
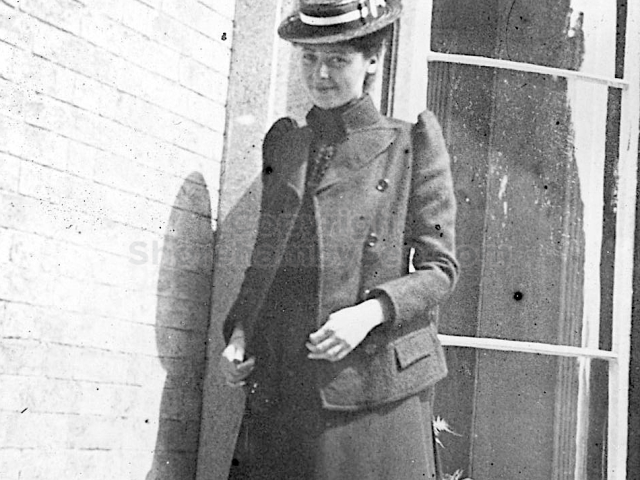
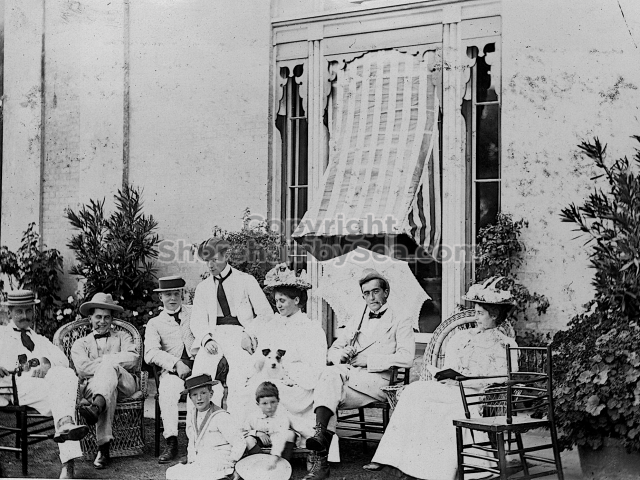
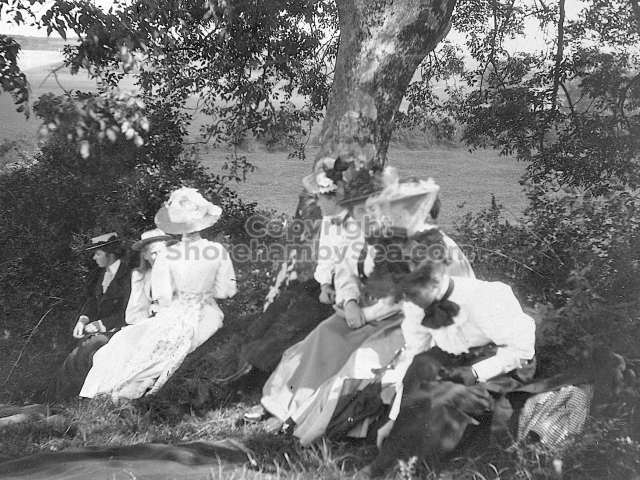
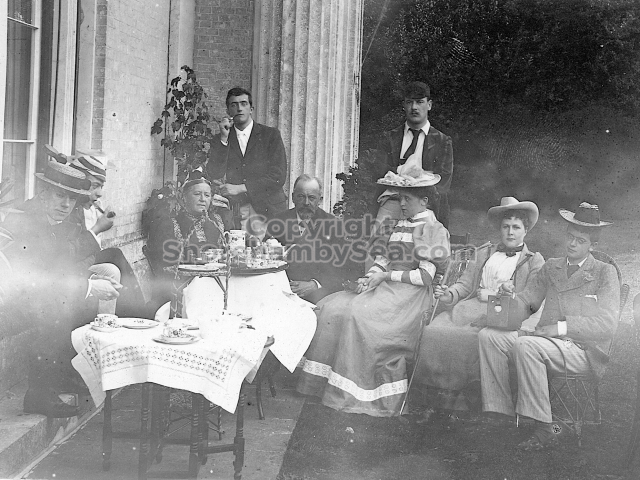
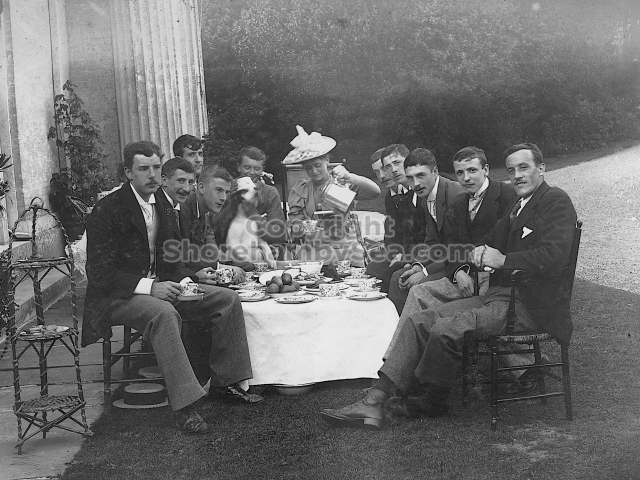
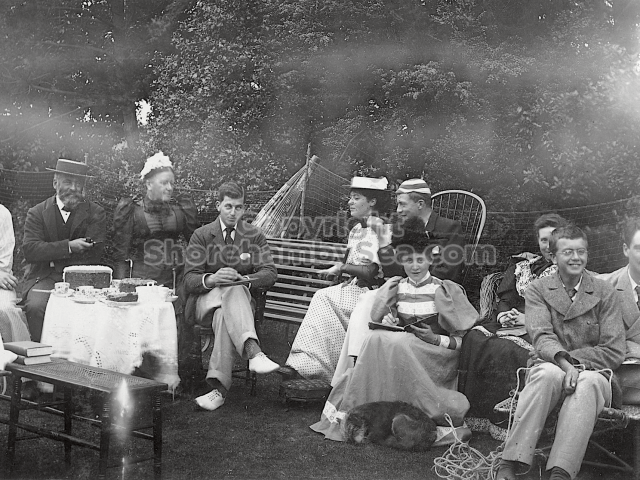
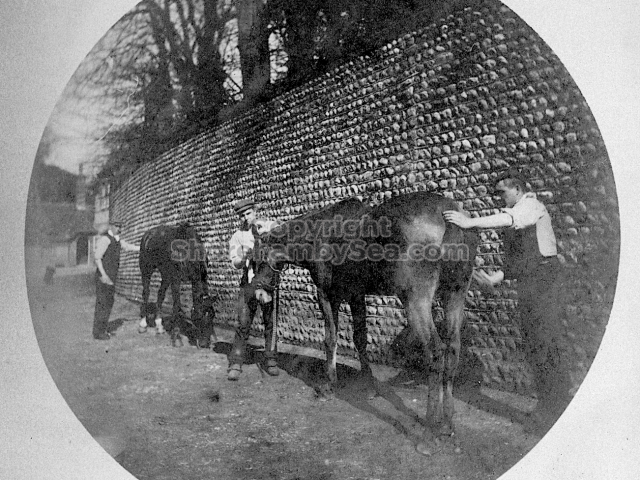
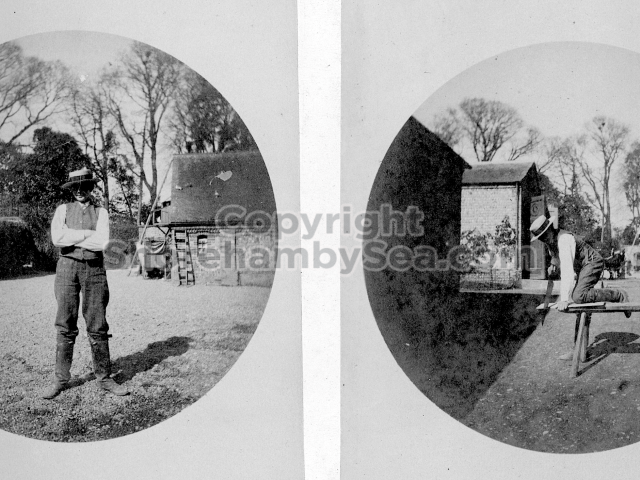
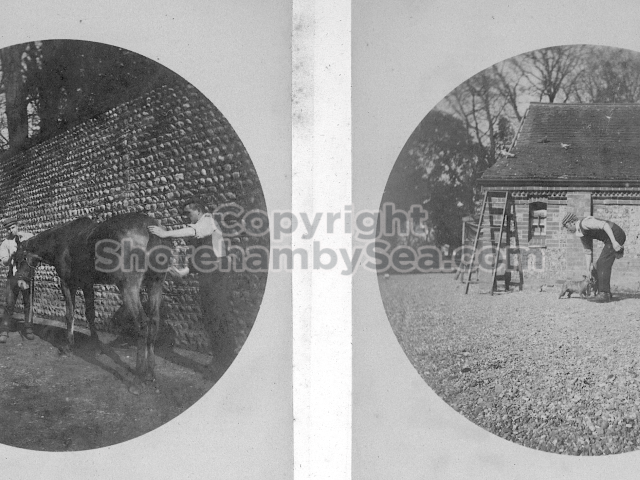
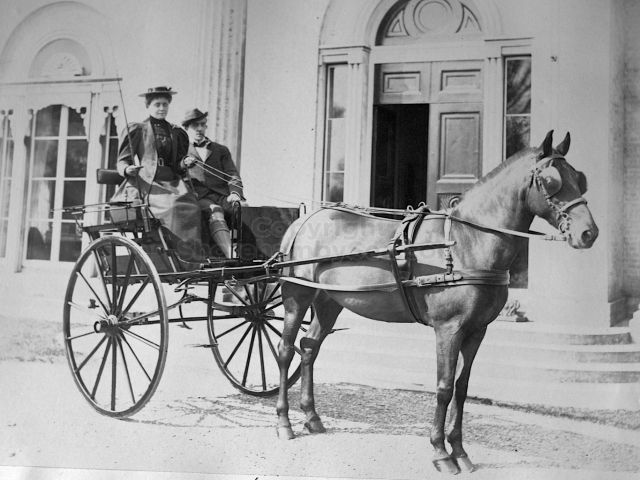
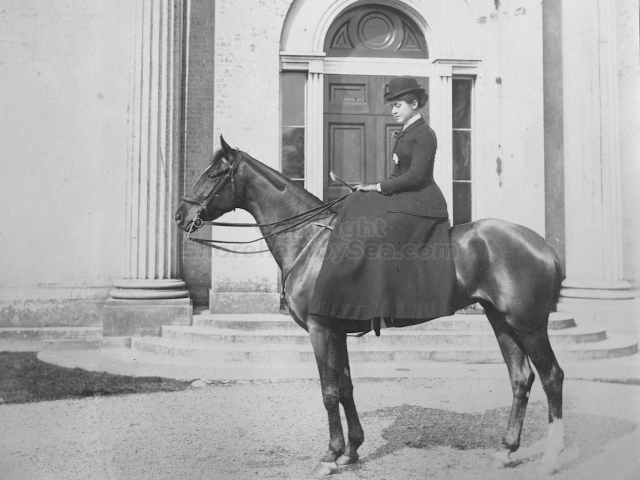
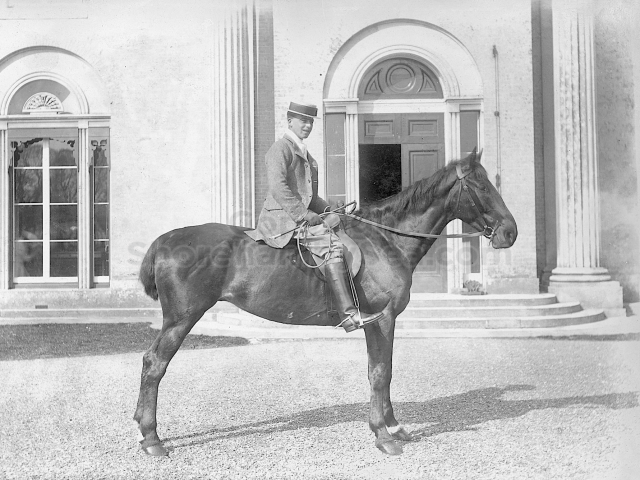
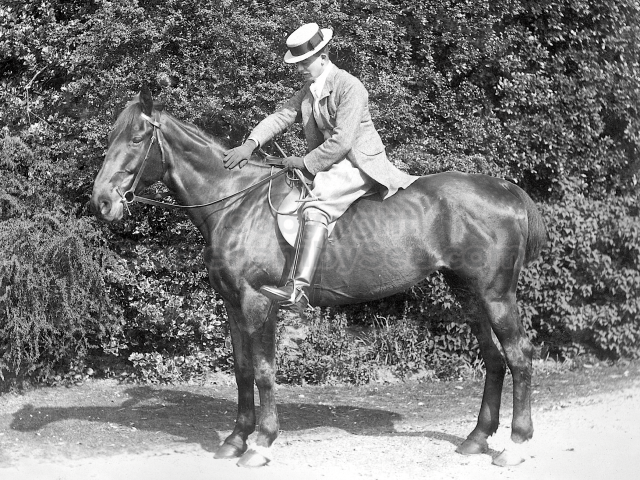
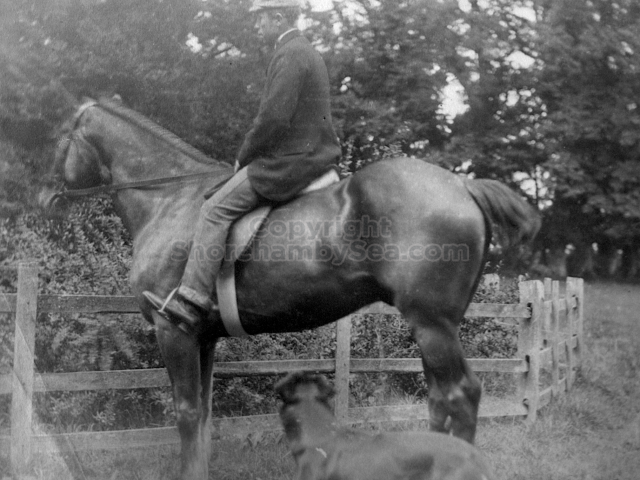
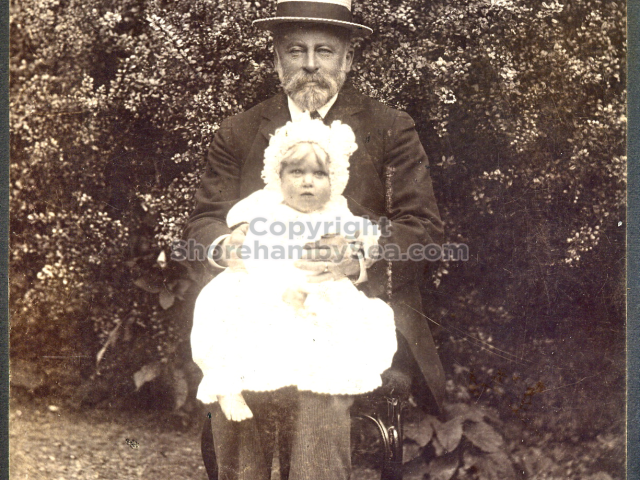
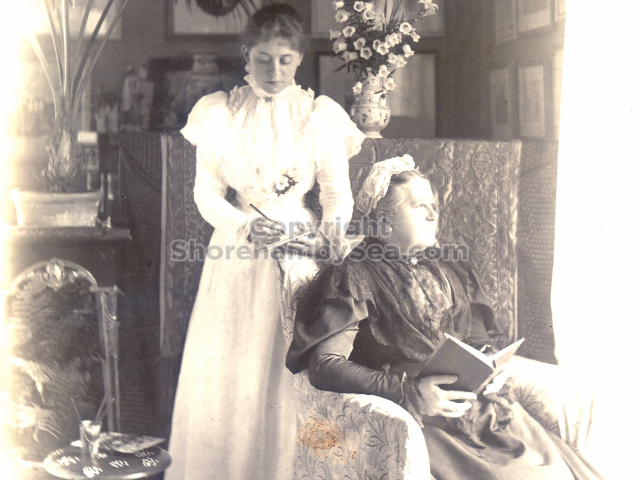
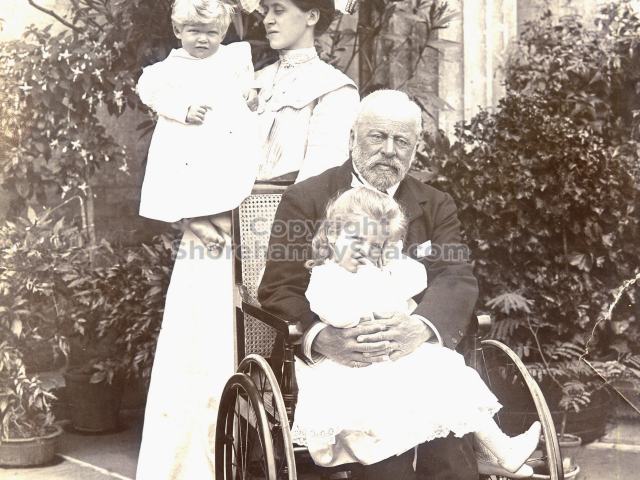
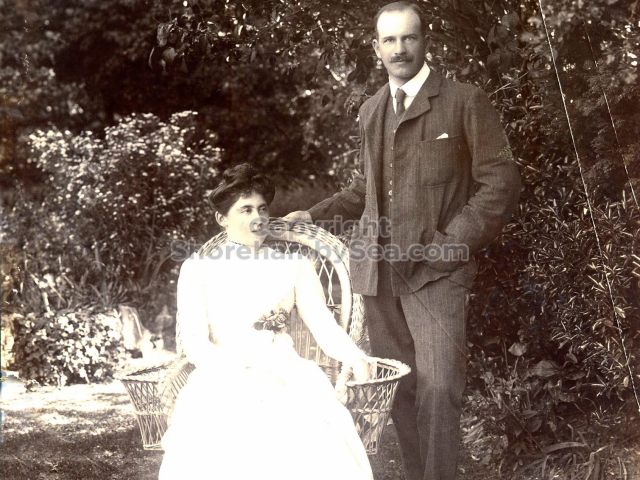
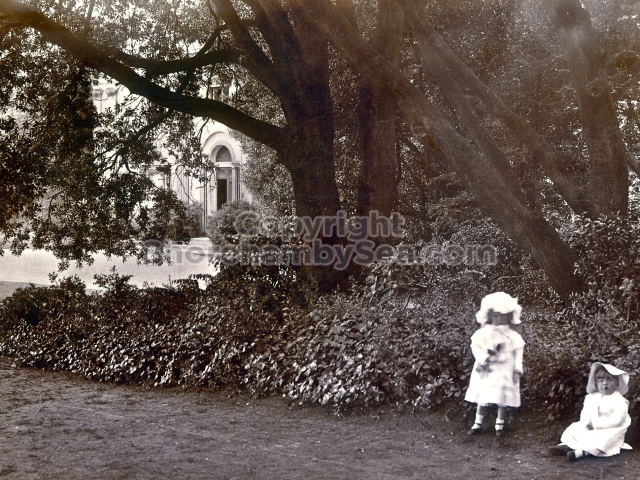
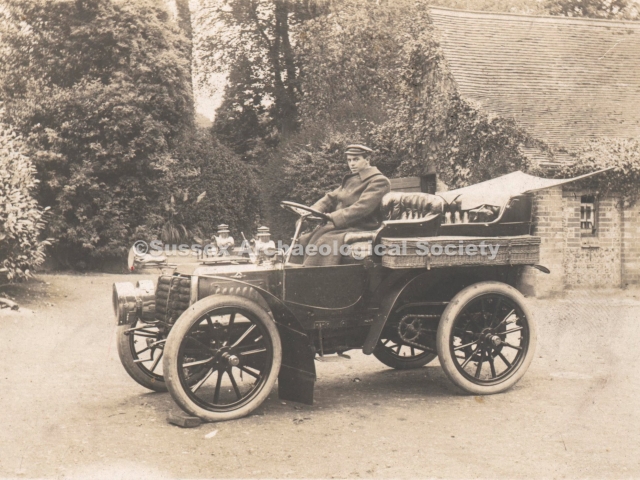
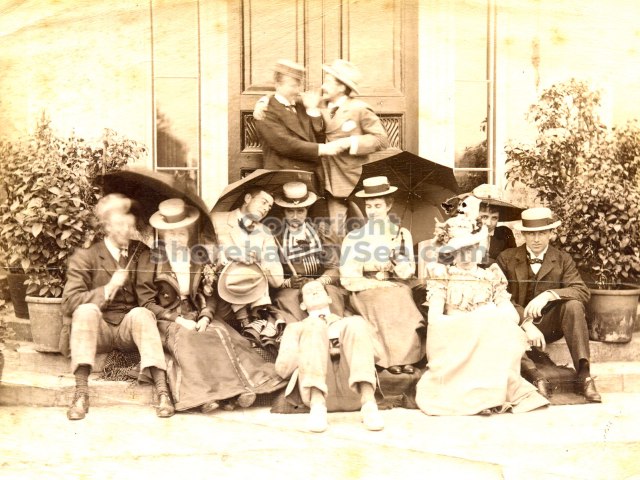
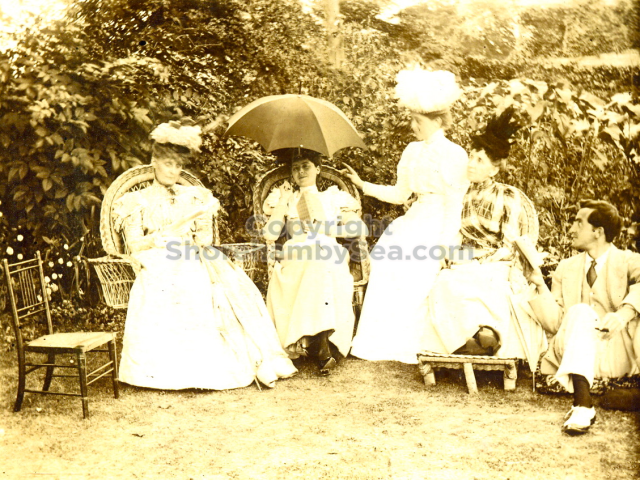
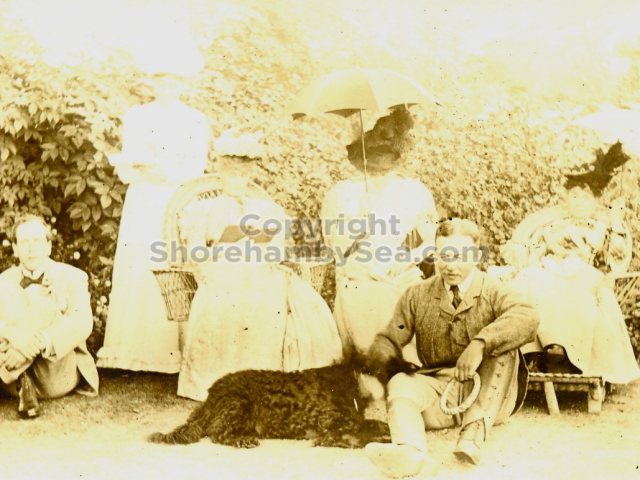
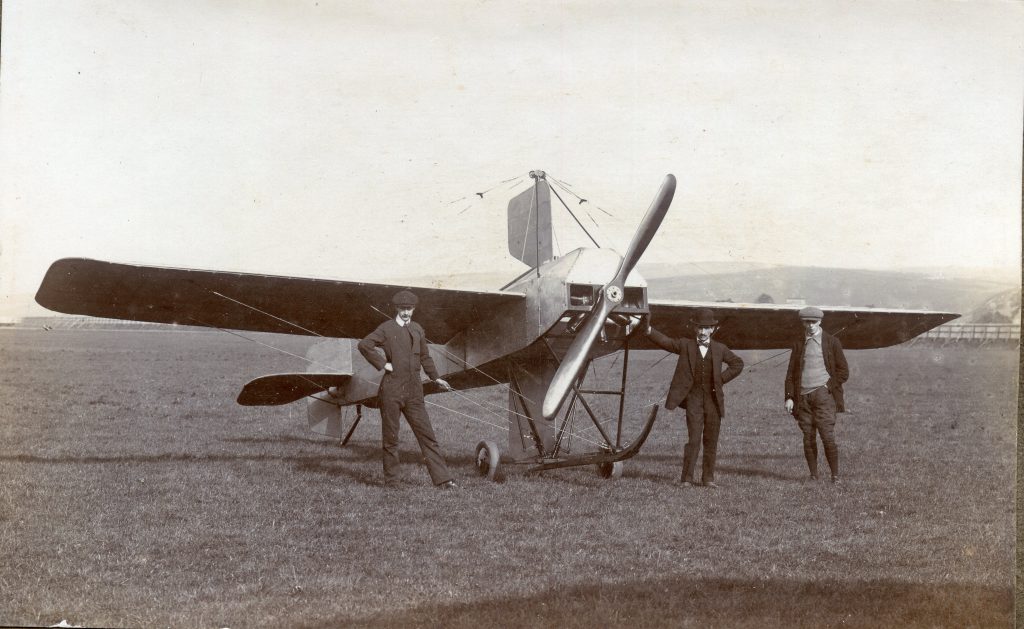
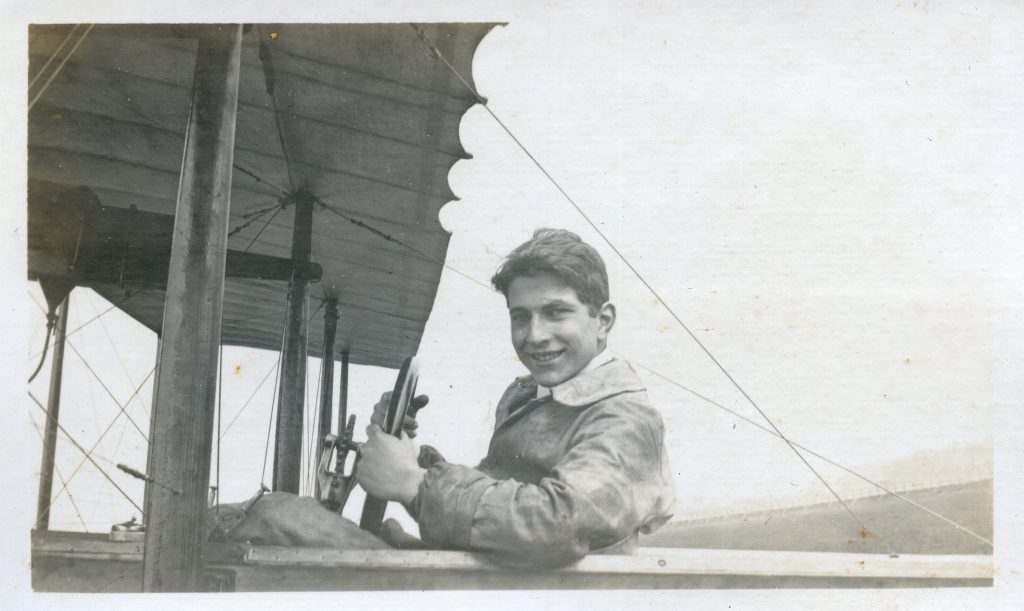
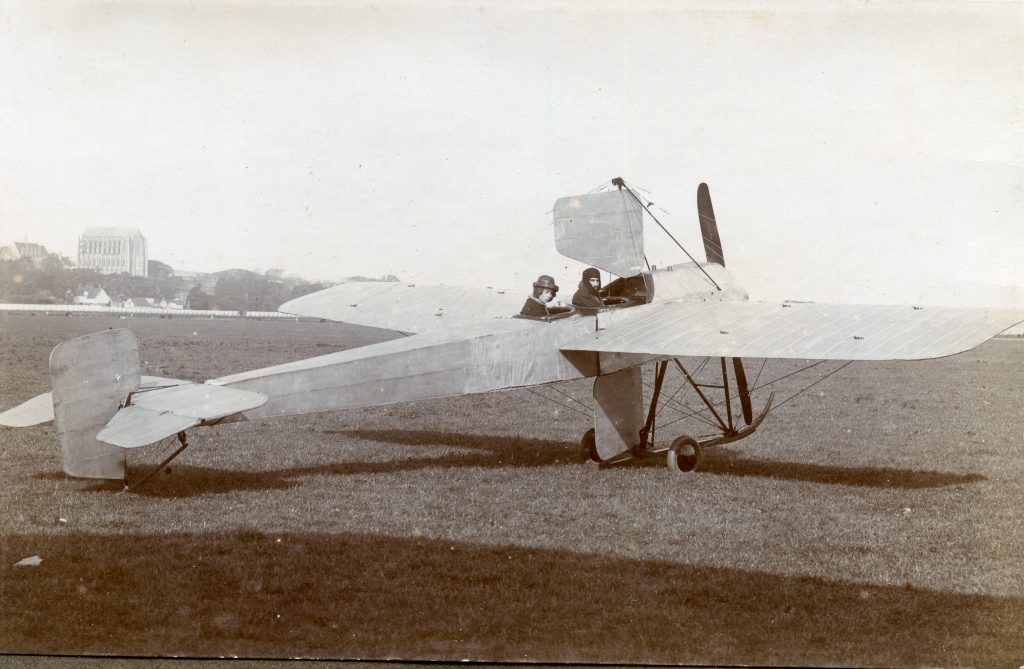
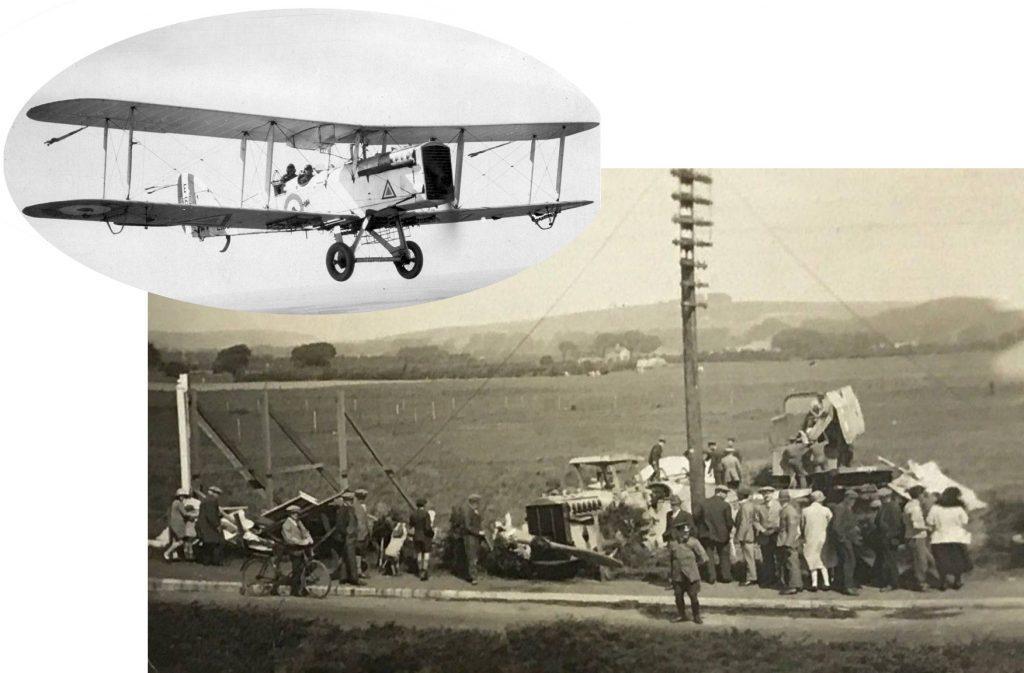
It is (was) three-quarter leather bound, about 100 mm thick in all, the boards approx, 370 x 298mm, with interleaved pages designed as a commercial scrap-book.It is clear that the Head boys were responsible for most of the snaps, but there are other more professional photos taken probably by William Page, Photographer, of Shoreham, whom Hester (Pinney) said she encouraged. There are also watercolours by Hester of a competent, but amateur quality, together with sundry printed items of interest, and photos of local views and personalities.
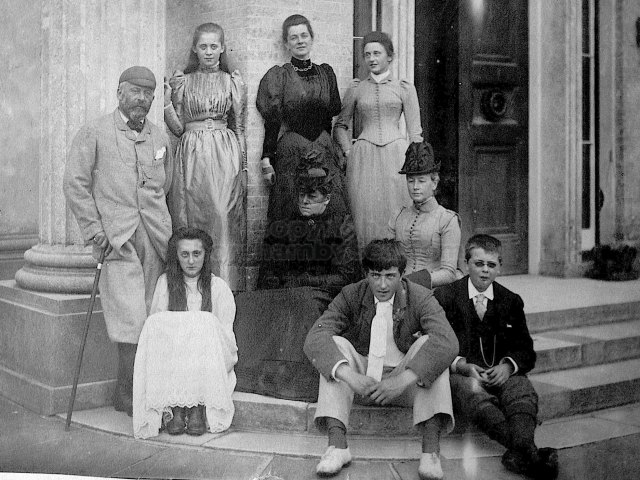
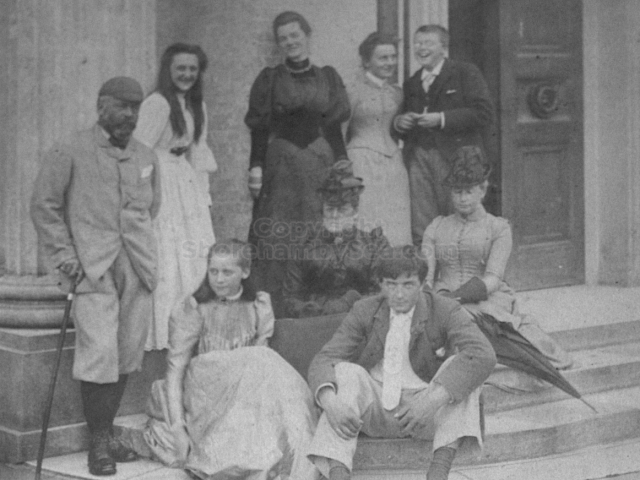
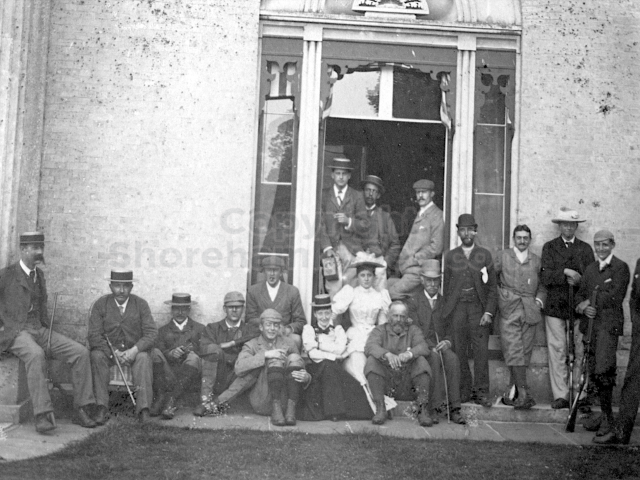
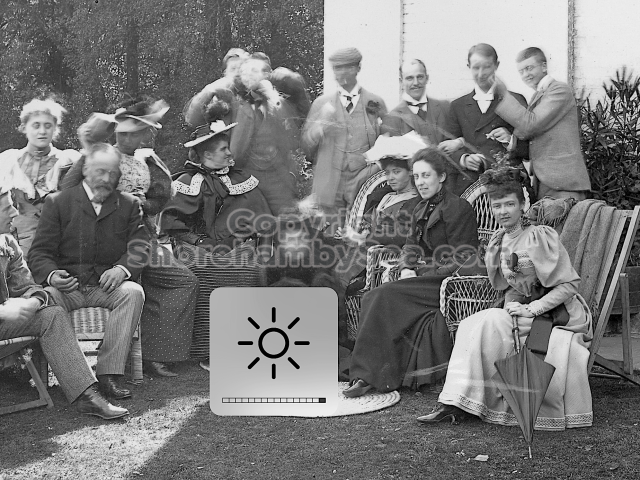
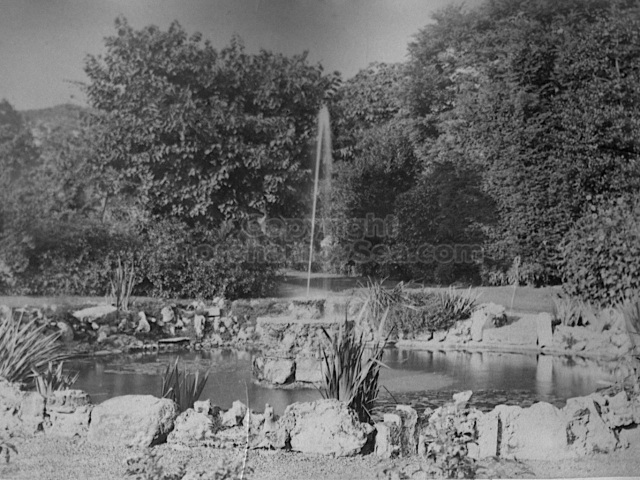
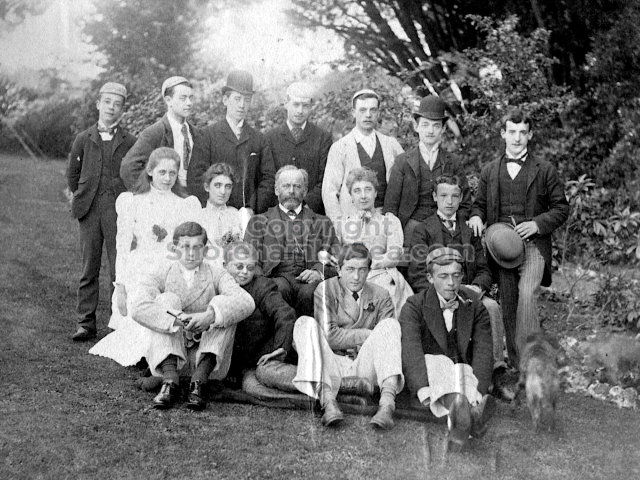
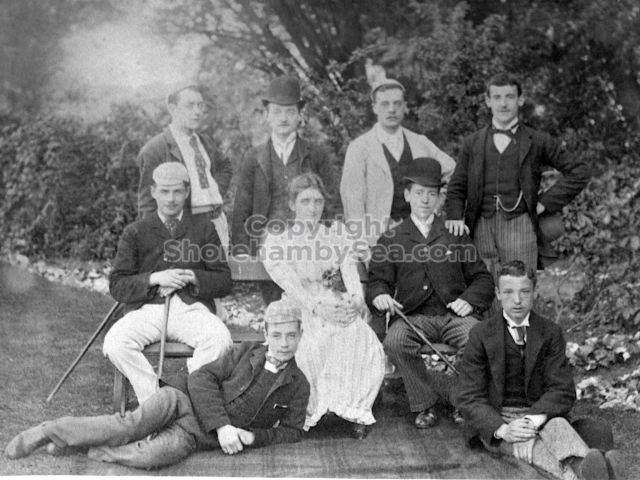
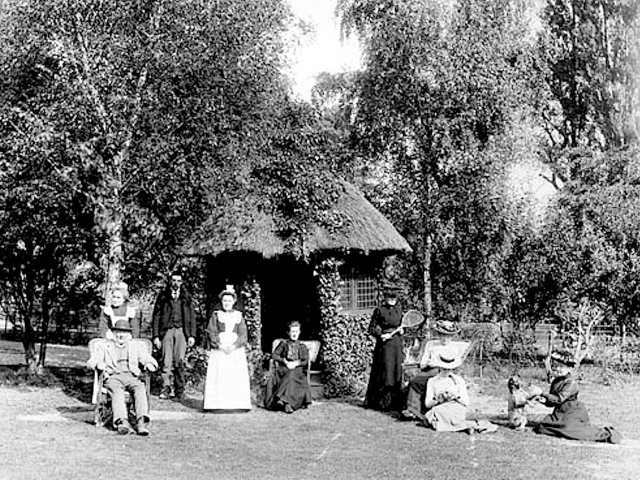
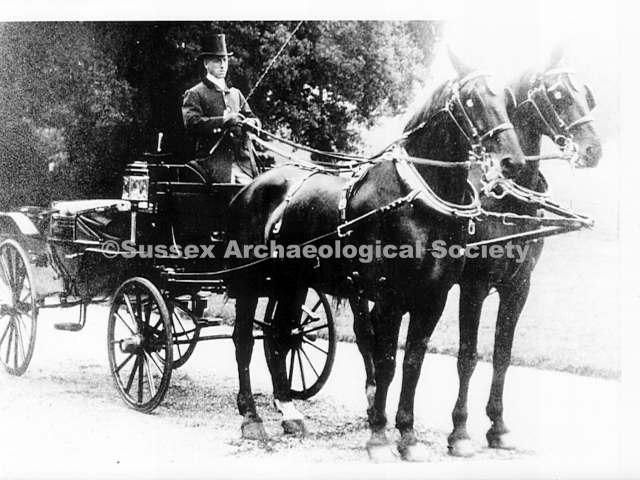
The whole gave a unique and fascinating view of the very happy life at Buckingham until Henry Head’s death in 1905, when the family quit Old Shoreham. The house lay empty and in 1911 was gutted, with the grounds occupied by a new house erected to the North.During their stay at Buckingham, the Heads effectively filled the role of ‘Lords of the Manor’ in the Town, and were most popular. Henry Head was an outgoing and generous personality, and he was clearly led by his very positive daughter Hester (Pinney), abetted by her brothers. The Park was regularly opened to the townsfolk, and Henry seems to have been the leader in the 1897 Diamond Jubilee celebrations. When, apart from a Grand March through the Town to a Fair and general festivities in the Park, there seems to have been a very early filrnshow in the field by the old Swiss Gardens. Fifty years later, Hester Pinney was stilt fondly rernembered in the Town.
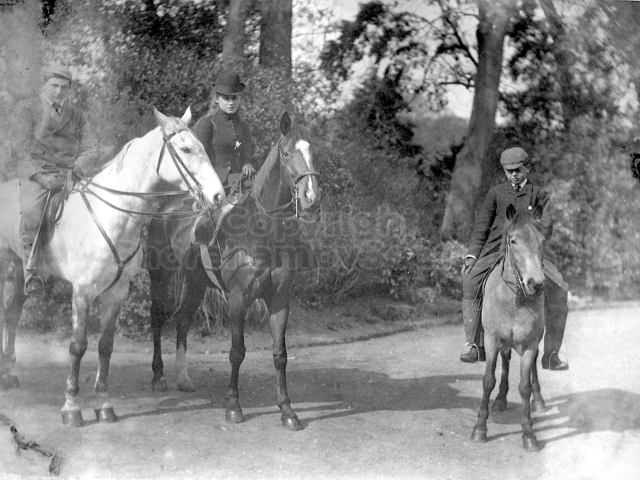
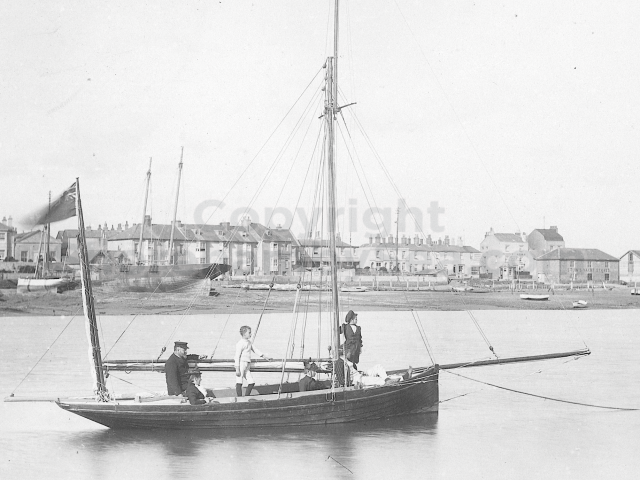
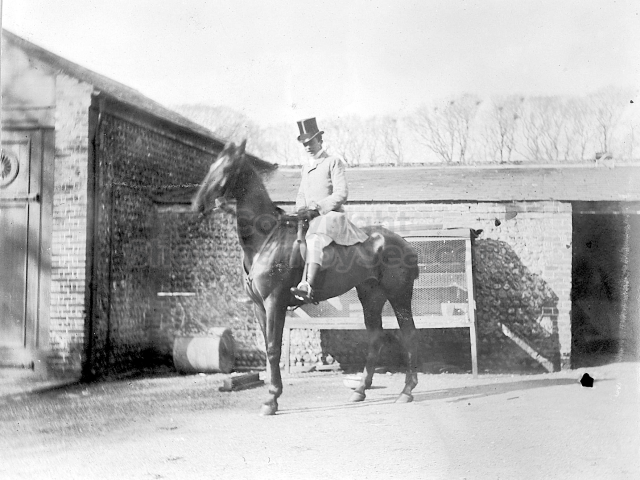
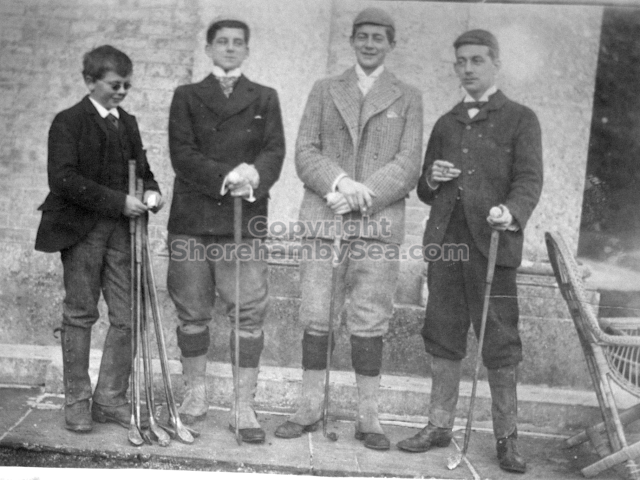
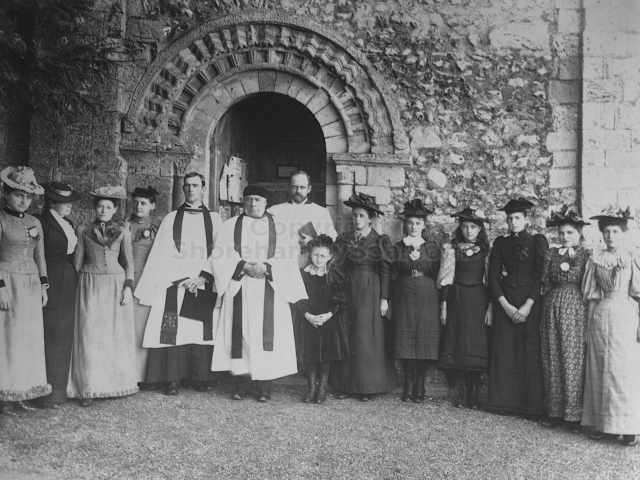
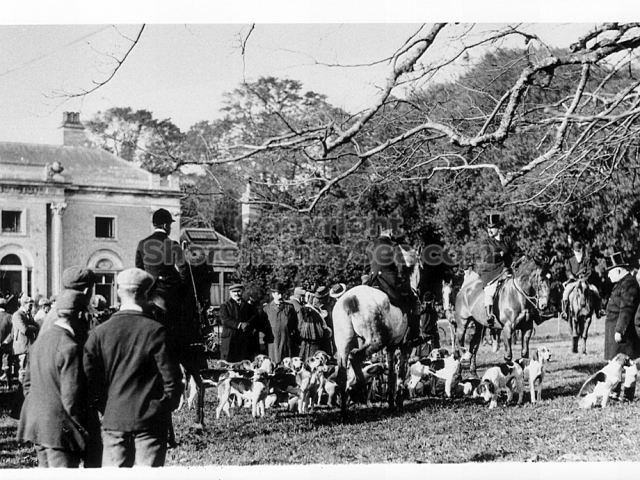
The Book records Hunting, Cricket, Yachting (Steam and Sail) Golf, Shooting, Riding, and alfresco entertainments.. The girls from the London Store, D. H. Evans, which the Heads owned, were also entertained in the Summer and are seen obviously enjoying themselves. The Book is a wonderful, unique, record of a lost age, which was soon to come to a tragic stop. One son was lost on the Titanic (sic Christopher Head), and one at Gallipoli (sic. Bernard Head); it is fitting that their memorials are in Old Shoreham Church, in the place that they so enjoyed.
Written by Michael Norman, date: post-1983